Psoriatic Arthritis Market Outlook
The high prevalence of psoriatic arthritis, which affects about 30% of people with psoriasis worldwide, plays a major role in driving the drug pipeline. This translates to roughly 37.5 million individuals globally. Due to the different types of psoriatic arthritis, effective treatments often require several clinical trials. This significant demand highlights the focus of pharmaceutical companies on developing new and effective therapies, broadening the treatment options available to patients.
Get a Free Sample Report with a Table of Contents:https://www.expertmarketresearch.com/clinical-trials/psoriatic-arthritis-drug-pipeline-analysis/requestsample
Psoriatic Arthritis: Introduction
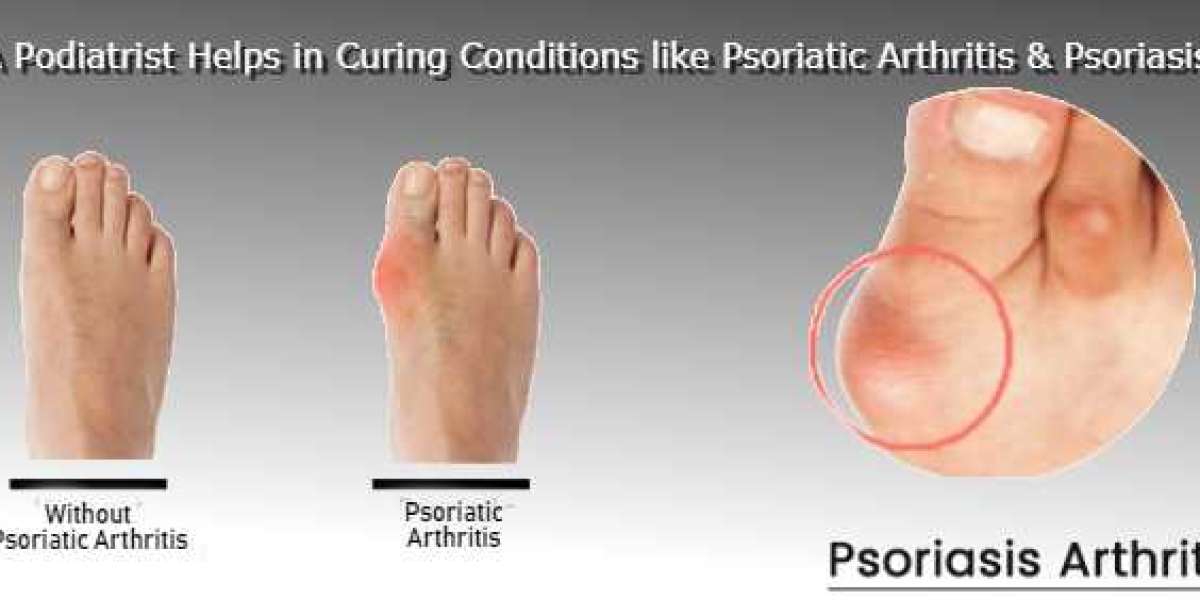
Psoriatic arthritis is a chronic autoimmune disease that causes joint inflammation and pain, often accompanied by skin psoriasis. It can affect any joint in the body, leading to stiffness, swelling, and reduced mobility. Symptoms may include fatigue, tender joints, and skin lesions, which can significantly impact daily activities and quality of life. While the exact cause remains unknown, genetic and environmental factors play a role. Early diagnosis and treatment are vital to managing the disease and preventing joint damage. Current treatments aim to control inflammation and improve function, with ongoing research focused on more effective and personalised therapies.
Psoriatic Arthritis Treatment Overview
Psoriatic arthritis is a chronic autoimmune condition characterised by joint inflammation, pain, and swelling, often accompanied by skin psoriasis. It can affect the spine, fingers, and toes, leading to stiffness, deformities, and reduced mobility. Early diagnosis is critical for managing symptoms and preventing permanent joint damage, which significantly impacts quality of life.
Treatment strategies depend on disease severity and patient needs. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) manage mild symptoms, while biologics and disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) target underlying inflammation. Emerging therapies, including targeted small molecules and monoclonal antibodies, offer tailored solutions for refractory or severe cases, improving patient outcomes and quality of life.
Read Full Report with Table of Contents: https://www.expertmarketresearch.com/clinical-trials/psoriatic-arthritis-drug-pipeline-analysis
Drug Pipeline Therapeutic Assessment
Analysis by Route of Administration
- Oral
- Parenteral
- Others
Analysis by Phase
- Preclinical Phase
- Phase I
- Phase II
- Phase III
- Phase IV
Analysis by Drug Class
- Recombinant Fusion Proteins
- Small Molecule
- Monoclonal Antibody
- Peptide
- Polymer
- Gene Therapy
Psoriatic Arthritis Drug Classes
Psoriatic arthritis treatments utilise a range of drug classes, each designed to target specific pathways and mechanisms involved in cancer growth and survival. These diverse classes enhance the effectiveness of therapy and contribute to personalised treatment strategies. Understanding these drug classes is essential for optimising patient outcomes.
1. Recombinant Fusion Proteins
Recombinant fusion proteins combine functional proteins into a single therapeutic molecule, targeting specific pathways in psoriatic arthritis. These drugs modulate immune activity, reducing inflammation and preventing joint damage. Their precision makes them a key option for managing moderate-to-severe cases effectively.
2. Small Molecule
Small molecule drugs are chemically synthesised compounds that disrupt specific pathways driving inflammation in psoriatic arthritis. These drugs, including Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors, offer oral treatment options that are easier to administer and effective in controlling symptoms, particularly in refractory cases.
3. Monoclonal Antibody
Monoclonal antibodies are biologically engineered proteins that target specific immune pathways, such as TNF-alpha or IL-17, to reduce inflammation in psoriatic arthritis. These therapies are highly effective in controlling severe symptoms and preventing joint damage, providing a cornerstone for modern treatment strategies.
4. Peptide
Peptide-based therapies use short chains of amino acids to modulate immune activity in psoriatic arthritis. By targeting specific signalling molecules, peptides help control inflammation and improve joint and skin symptoms. These therapies are being developed as precise and minimally invasive options.
5. Polymer
Polymer-based therapies enhance drug delivery and stability, ensuring targeted treatment of inflammation in psoriatic arthritis. These systems reduce side effects by concentrating therapeutic agents at the affected sites, improving efficacy and patient outcomes.
6. Gene Therapy
Gene therapy aims to address the genetic basis of psoriatic arthritis by modifying or silencing specific genes involved in immune dysfunction. This innovative approach offers the potential for long-term remission and represents a promising frontier in personalised treatment for autoimmune diseases.
Psoriatic Arthritis- Pipeline Drug Profiles
This section provides an overview of the various drugs used in the treatment of psoriatic arthritis. It covers their classifications, mechanisms of action, and methods of administration, offering essential insights for effective treatment strategies.
1. Izokibep
Izokibep, a small IL-17A inhibitor, is designed to reduce inflammation and control symptoms in psoriatic arthritis. Its unique design allows for improved tissue penetration and potency compared to conventional biologics. Clinical trials have shown promising results in reducing joint pain and swelling, making it a potential breakthrough therapy for refractory cases.
2. HS-10374
HS-10374 is a small molecule drug under development for psoriatic arthritis. It targets key inflammatory pathways involved in the disease process, offering a new oral treatment option. Preclinical studies suggest its effectiveness in controlling inflammation and slowing disease progression, addressing the unmet need for easier-to-administer therapies.
3. Secukinumab
Secukinumab is a monoclonal antibody targeting IL-17A, a key driver of inflammation in psoriatic arthritis. It has demonstrated efficacy in reducing joint and skin symptoms, improving patient quality of life. Approved for moderate-to-severe cases, Secukinumab remains a cornerstone of biologic therapy, offering durable symptom control and preventing disease progression.
Psoriatic Arthritis: Competitor Landscape
The key features of the report include patent analysis, clinical trials, grants analysis, funding and investment analysis, partnerships, and collaborations analysis by the leading key players. The major companies in the market are as follows:
ACELYRIN Inc.
ACELYRIN, headquartered in Agoura Hills, California, focuses on developing advanced immunology therapies, including treatments for psoriatic arthritis. Their pipeline includes innovative biologics targeting IL-17 and other pathways, aiming to improve efficacy and safety profiles. ACELYRIN’s commitment to patient-centric solutions positions them as a rising player in autoimmune disease treatment.
Hansoh BioMedical RD Company
Hansoh BioMedical RD Company, based in Lianyungang, China, is a leader in pharmaceutical innovation, developing treatments for autoimmune diseases like psoriatic arthritis. Their research focuses on small molecule drugs that address inflammation at the molecular level. Hansoh’s commitment to affordability and accessibility makes them a significant contributor to advancing care worldwide.
Novartis Pharmaceuticals
Novartis, headquartered in Basel, Switzerland, is a global leader in developing therapies for autoimmune diseases. Their flagship drug Secukinumab has transformed psoriatic arthritis treatment by targeting IL-17A. Novartis continues to innovate with new drugs and combination therapies, aiming to improve outcomes for patients with severe or refractory disease.
Other key players in the landscape include MoonLake Immunotherapeutics AG, Aclaris Therapeutics, Inc., Ventyx Biosciences, Inc., Enlivex Therapeutics Ltd., AbbVie, and Janssen Research Development, LLC.
We at Expert Market Research always strive to provide you with the latest information. The numbers in the article are only indicative and may be different from the actual report.