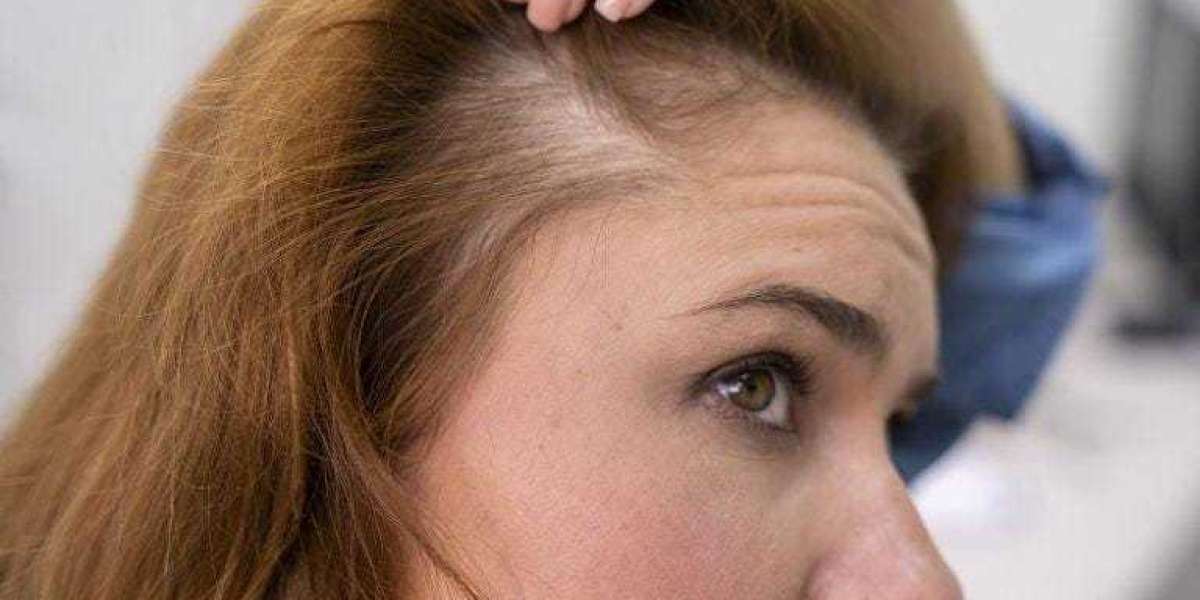
Hair loss can be a distressing experience, affecting both self-esteem and confidence. For many people, especially men experiencing male pattern baldness, finding effective treatment options is a top priority. Finasteride, a widely recognized medication, has become a go-to solution for combating hair loss. Before starting treatment, it’s essential to understand how finasteride works, its potential benefits and side effects, and important considerations to keep in mind.
What is Finasteride?
Finasteride For Hair Loss Dubaiis a prescription medication primarily used to treat conditions like benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and male pattern baldness. Its primary mechanism involves inhibiting an enzyme known as 5-alpha-reductase. This enzyme converts testosterone into dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a hormone linked to hair loss. By reducing DHT levels, finasteride helps slow hair loss and even promotes hair regrowth in some individuals.
How Effective is Finasteride for Hair Loss?
Finasteride has been proven to be highly effective in clinical studies. For individuals experiencing male pattern baldness, approximately 80-90% report positive outcomes when using finasteride. These outcomes often include:
Slowing Down Hair Loss: The medication can halt or slow the progression of hair loss.
Promoting Hair Regrowth: Many users see an increase in hair density, particularly in the crown and middle scalp areas.
Improving Hair Thickness: Regular use can result in thicker hair strands.
However, it’s important to set realistic expectations. Finasteride works best when used consistently over long periods and is more effective at addressing hair loss in the earlier stages of baldness.
How Should You Take Finasteride?
Finasteride is typically available in 1 mg and 5 mg doses. For hair loss treatment, the standard dosage is 1 mg per day. It can be taken with or without food, and most individuals will notice results within 3-6 months of starting the treatment. Full benefits can often take up to a year or more to become apparent.
Potential Side Effects of Finasteride:
While finasteride is generally well-tolerated, it is not without its potential side effects. These can include:
Sexual Side Effects: Some users report a decrease in libido, erectile dysfunction, and reduced semen volume. Though these symptoms can be concerning, they are relatively uncommon and often temporary.
Hormonal Changes: By altering DHT levels, finasteride can impact other hormones, potentially leading to changes in mood, breast tenderness, or gynecomastia (enlarged breast tissue).
Rare Side Effects: More severe, yet rare, side effects may include depression and allergic reactions.
It's important to consult with a healthcare provider to assess these potential risks and decide if finasteride is the right treatment for you.
Who Should Consider Finasteride?
Finasteride is generally recommended for individuals experiencing male pattern baldness, which typically begins in the late 20s to early 30s. Ideal candidates include:
Men in the Early Stages of Hair Loss: Those who have just started to notice hair thinning are more likely to benefit from finasteride.
People with Family History of Hair Loss: Genetic predisposition to hair loss makes finasteride a viable option for those whose relatives have experienced similar issues.
However, finasteride is not recommended for women, especially those who are pregnant or may become pregnant, as it can lead to birth defects in male fetuses.
Important Considerations Before Starting Treatment:
Consult Your Doctor: Before starting finasteride, it’s essential to have an open discussion with a healthcare professional. They can evaluate your medical history, potential interactions with other medications, and any underlying conditions.
Monitor for Side Effects: Regular follow-ups with your doctor can help detect and manage any adverse effects early on. This is crucial for assessing whether continued use is safe and beneficial.
Understand the Commitment: Hair loss treatment with finasteride is a long-term commitment. If you stop taking the medication, any gains made in hair growth typically diminish within 12 months, and the user may revert to their previous state of hair loss.
Weigh the Risks and Benefits: While many users find success with finasteride, others may experience side effects that outweigh the benefits. Weighing these risks is crucial in making an informed decision.
Alternatives to Finasteride:
If finasteride does not seem like the right option, other treatments for hair loss include:
Minoxidil: An over-the-counter topical solution that helps promote hair growth by increasing blood flow to the scalp.
Hair Transplant Surgery: For those seeking permanent solutions, hair transplants can be effective in restoring hair in areas of thinning.
Lifestyle Changes: Ensuring a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management can contribute to overall hair health.
Final Thoughts:
Finasteride For Hair Lossis an effective treatment for many individuals struggling with hair loss, but it’s not suitable for everyone. Understanding the potential benefits and risks, and consulting with a qualified healthcare provider, is vital to making the right choice. If you’re considering finasteride as a hair loss treatment, taking the time to weigh these factors will help you make an informed decision that best aligns with your needs and goals.