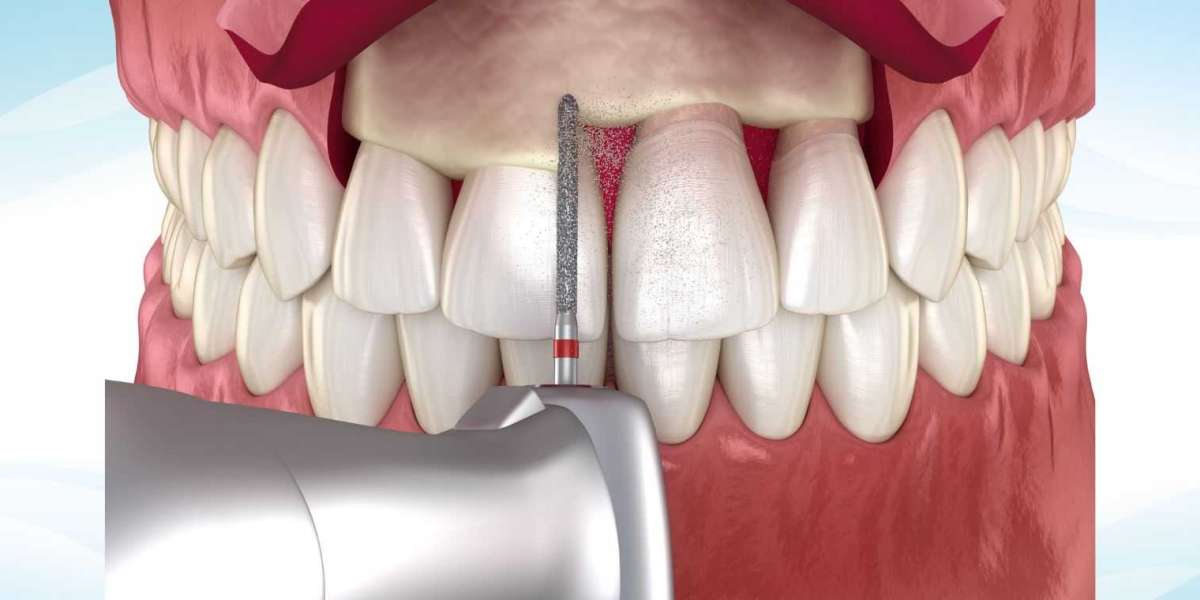
Gingivectomy is an effective treatment for gum disease, especially when the condition has advanced beyond the scope of nonsurgical treatments. When gum disease reaches a certain severity, traditional methods like deep cleaning may no longer be sufficient. Gum Tissue Removal involves the removal of infected or overgrown gum tissue to promote healing and improve overall oral health. This procedure can significantly help restore gum health, prevent further disease progression, and improve the overall appearance of the gums.
What is Gingivectomy?
Gingivectomy is a surgical procedure that involves the removal of diseased or excess gum tissue. It is typically recommended when gum disease, such as periodontitis, has caused severe gum infections, deep pockets, and inflammation that are not responding to nonsurgical treatments like scaling and root planing. By eliminating infected tissue, gingivectomy reduces the spread of the disease and helps the gums heal properly.
Key factors that make gingivectomy effective include:
- Removal of infected tissue: Gingivectomy removes bacteria-laden tissue, preventing further infection.
- Promotes gum healing: By cleaning and reshaping the gums, the procedure allows for more effective healing.
- Prevents tooth loss: If gum disease is left untreated, it can lead to tooth loss. Gingivectomy helps prevent this by addressing the root cause of the infection.
The procedure is often a vital part of the treatment plan when other methods have failed.
When is Gingivectomy Necessary for Gum Disease?
Gingivectomy is generally recommended for patients who have advanced gum disease, particularly when other nonsurgical treatments have proven ineffective. It is particularly beneficial for patients with gum disease who are experiencing deep pockets, gum recession, and significant tissue damage.
Here are some scenarios where gingivectomy may be necessary:
- Severe gum disease: When gum disease has reached an advanced stage with deep pockets between the teeth and gums.
- Overgrown gum tissue: In cases where gum tissue has overgrown due to certain medications or conditions, affecting the ability to clean the teeth effectively.
- Persistent infection: If scaling and root planing fail to resolve the infection, gingivectomy can help remove the source of bacteria.
- Cosmetic concerns: For patients with uneven gums caused by gum disease, gingivectomy can reshape the gum line for a more aesthetically pleasing smile.
Gingivectomy offers a solution when more conservative treatments are no longer enough to manage gum disease.
How Does Gingivectomy Help in Treating Gum Disease?
Gingivectomy helps in treating gum disease by removing the infected tissue that harbors bacteria and reduces the size of the gum pockets around teeth. This reduces the risk of further bacterial growth and promotes healthier gum tissue, preventing the spread of infection to the tooth roots or underlying bone.
The primary benefits of gingivectomy in treating gum disease include:
- Reduction of gum pockets: The procedure removes infected tissue and helps shrink the pockets around the teeth, making it easier to maintain oral hygiene.
- Improvement in gum health: By eliminating infected tissue, gingivectomy allows healthy gum tissue to regenerate and reattach to the teeth.
- Prevention of further infection: By cleaning out the bacteria and diseased tissue, gingivectomy minimizes the chances of the infection spreading.
- Support for bone health: In advanced gum disease, the infection can also affect the bone structure. By reducing infection and promoting healing, gingivectomy helps maintain the bone’s integrity.
These effects can significantly improve the prognosis for patients suffering from severe gum disease.
What to Expect During the Gingivectomy Procedure?
The gingivectomy procedure is typically performed under local anesthesia, which ensures that the patient remains comfortable throughout the process. The length of the procedure depends on the extent of gum tissue removal, but it generally takes around one to two hours to complete.
The key steps involved in the gingivectomy procedure are as follows:
- Examination and planning: Your dentist will first examine your gums and determine the extent of the infection and the amount of tissue that needs to be removed.
- Anesthesia: Local anesthesia is applied to numb the treatment area, ensuring a pain-free experience during the procedure.
- Tissue removal: The dentist uses specialized tools to remove the infected or overgrown gum tissue.
- Shaping the gum line: Once the tissue is removed, the dentist will reshape the gum line to ensure it is even and aesthetically pleasing.
- Aftercare instructions: Post-operative care instructions are given to ensure proper healing, including pain management, oral hygiene tips, and a recommended diet.
Patients may feel mild discomfort for a few days following the procedure, but the recovery process is usually quick.
Post-Operative Care After Gingivectomy:
Proper post-operative care is crucial for the successful healing of the gums after a gingivectomy. Following the dentist’s instructions can help minimize discomfort, prevent complications, and ensure that the procedure is as effective as possible.
Here are some tips for aftercare following a gingivectomy:
- Pain management: Over-the-counter pain relievers or prescribed medications can help manage any pain or swelling in the days following the procedure.
- Dietary restrictions: Stick to a soft-food diet and avoid hard, crunchy, or spicy foods that could irritate the healing gums.
- Avoid smoking: Smoking can slow down the healing process and increase the risk of infection.
- Good oral hygiene: Gently brush your teeth, but avoid brushing the treated area directly until your gums have healed.
- Saltwater rinses: Rinsing with saltwater can help reduce swelling and promote healing.
By following these instructions, you can ensure a smooth recovery and support the success of the procedure.
Risks and Considerations of Gingivectomy:
While Gingivectomy (Gum Tissue Removal) is generally a safe and effective treatment for gum disease, there are some risks and considerations to keep in mind. These risks are rare but can occur, especially if proper aftercare is not followed.
Some potential risks and considerations include:
- Infection: As with any surgical procedure, there is a risk of infection if the wound site is not cared for properly.
- Bleeding: Minor bleeding is normal after a gingivectomy, but excessive or prolonged bleeding should be reported to your dentist.
- Pain and discomfort: Some patients may experience mild to moderate pain and discomfort during the recovery period, but this can usually be managed with pain relievers.
- Gum recession: Although rare, gum recession can occur after the procedure, especially if too much tissue is removed.
Understanding these risks and being prepared can help you make informed decisions and reduce any potential concerns.
Conclusion:
Gingivectomy is an effective treatment for gum disease, particularly when the infection is severe and other treatments have failed. By removing infected gum tissue, reshaping the gums, and promoting healthier tissue growth, this procedure can restore gum health and prevent further disease progression. In addition to its medical benefits, gingivectomy can improve the overall appearance of the gums, making it an essential tool in both health and aesthetic dentistry. If you are dealing with advanced gum disease, consult your dentist to see if gingivectomy is the right solution for you.