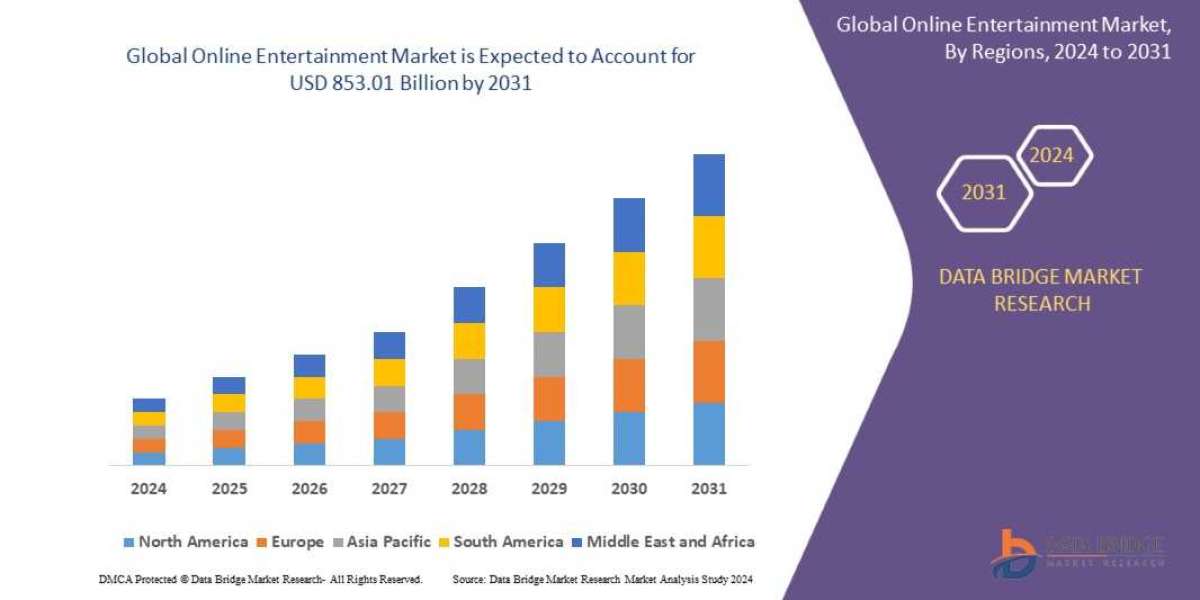
The Online Entertainment Market sector is undergoing rapid transformation, with significant growth and innovations expected by 2031. In-depth market research offers a thorough analysis of market size, share, and emerging trends, providing essential insights into its expansion potential. The report explores market segmentation and definitions, emphasizing key components and growth drivers. Through the use of SWOT and PESTEL analyses, it evaluates the sector’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, while considering political, economic, social, technological, environmental, and legal influences. Expert evaluations of competitor strategies and recent developments shed light on geographical trends and forecast the market’s future direction, creating a solid framework for strategic planning and investment decisions.
Get a Sample PDF of Report - https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/request-a-sample/?dbmr=global-online-entertainment-market
Which are the top companies operating in the Online Entertainment Market?
The report profiles noticeable organizations working in the water purifier showcase and the triumphant methodologies received by them. It likewise reveals insights about the share held by each organization and their contribution to the market's extension. This Global Online Entertainment Market report provides the information of the Top Companies in Online Entertainment Market in the market their business strategy, financial situation etc.
Amazon Web Services, Inc. (U.S.), Netflix (U.S.), Google LLC (U.S.), Sony Group Corporation (Japan), King (U.K.), Spotify AB (Sweden), Rakuten Group, Inc. (Japan), CBS Corporation (U.S.), Comcast (U.S.), Disney (U.S.), Charter Communications (U.S.)
Report Scope and Market Segmentation
Which are the driving factors of the Online Entertainment Market?
The driving factors of the Online Entertainment Market are multifaceted and crucial for its growth and development. Technological advancements play a significant role by enhancing product efficiency, reducing costs, and introducing innovative features that cater to evolving consumer demands. Rising consumer interest and demand for keyword-related products and services further fuel market expansion. Favorable economic conditions, including increased disposable incomes, enable higher consumer spending, which benefits the market. Supportive regulatory environments, with policies that provide incentives and subsidies, also encourage growth, while globalization opens new opportunities by expanding market reach and international trade.
Online Entertainment Market - Competitive and Segmentation Analysis:
**Segments**
- By Device Type: The online entertainment market can be segmented based on the device type into mobile devices, desktops, and laptops. With the increasing penetration of smartphones and easy access to the internet, mobile devices are becoming a popular choice for consuming online entertainment content.
- By Revenue Model: This segment includes subscription-based revenue models, advertising-based revenue models, and transaction-based revenue models. Subscription-based models are gaining traction due to the convenience and value they offer to consumers, while advertising-based models continue to be a significant revenue driver for online entertainment platforms.
- By Content Type: Content types in the online entertainment market consist of audio content, video content, gaming content, and live streaming content. Video content remains the dominant segment due to the popularity of platforms like YouTube, Netflix, and Amazon Prime Video, while gaming content is experiencing rapid growth with the rise of esports and mobile gaming.
**Market Players**
- Netflix Inc.: Netflix is a leading player in the global online entertainment market, offering a wide range of movies, series, and original content to subscribers worldwide. The company's focus on quality content and user experience has helped it maintain its competitive position in the market.
- Amazon.com Inc.: Amazon's Prime Video service has emerged as a strong competitor to Netflix, leveraging its existing customer base and e-commerce platform to drive subscriptions. The company's investment in original content production has helped it attract a loyal user base.
- Tencent Holdings Limited: Tencent is a key player in the online gaming segment, with popular titles like Honor of Kings and PUBG Mobile driving its revenue growth. The company's investment in music streaming and video content platforms also positions it well in the online entertainment market.
- Google LLC: Google's YouTube platform is a dominant force in the online video content segment, attracting billions of users every month. The company's advertising revenue model and creator ecosystem have cemented its position as a leading player in the online entertainment space.
The global online entertainment market is poised for significant growthThe online entertainment market is witnessing a rapid evolution driven by advancements in technology and changing consumer preferences. Segmentation of the market based on device type reveals a shift towards mobile devices as the preferred choice for accessing online entertainment content. The widespread adoption of smartphones and the increasing availability of high-speed internet have transformed how consumers engage with entertainment platforms. This trend underscores the importance for market players to optimize their offerings for mobile devices to cater to the growing demand for on-the-go entertainment experiences.
Revenue models play a crucial role in shaping the online entertainment landscape, with subscription-based models gaining prominence due to their ability to provide a seamless and ad-free viewing experience for consumers. Subscription services such as Netflix and Amazon Prime Video have disrupted traditional media consumption habits by offering a vast library of content for a fixed monthly fee. In contrast, advertising-based models continue to be a significant source of revenue for online entertainment platforms, leveraging targeted advertising to monetize user engagement effectively. The coexistence of different revenue models highlights the need for market players to diversify their monetization strategies to maximize profitability and sustain long-term growth.
Content type segmentation sheds light on the diverse offerings within the online entertainment market, with video content emerging as the dominant segment driven by popular streaming platforms like YouTube and Netflix. The demand for high-quality video content continues to rise, fueled by the increasing popularity of original series and movies produced by online streaming services. Gaming content is another rapidly growing segment, fueled by the proliferation of esports and mobile gaming platforms that attract a global audience of gamers. Live streaming content is also gaining traction, with platforms like Twitch providing opportunities for content creators to engage with their audiences in real-time.
Market players such as Netflix, Amazon.com, Tencent Holdings, and Google are at the forefront of driving innovation and shaping the competitive landscape of the online entertainment market. These companies have leveraged their technological expertise and content offerings to attract and retain a loyal user base. Netflix's focus on original content and user experience, Amazon's integration of Prime Video with its e-commerce platformThe global online entertainment market is on a trajectory for significant growth, fueled by technological advancements and shifting consumer behaviors. The market segmentation based on device type highlights the increasing preference for mobile devices, reflecting the ubiquitous nature of smartphones and the convenience of accessing entertainment content on-the-go. This trend underscores the importance for market players to tailor their offerings to mobile platforms to meet the evolving needs of consumers who seek seamless and flexible entertainment experiences.
Revenue models are a pivotal aspect of the online entertainment market, with subscription-based models gaining traction due to their ability to offer ad-free and personalized content consumption experiences. Platforms like Netflix and Amazon Prime Video have revolutionized the way users access and consume media by offering a vast library of content for a fixed monthly fee. On the other hand, advertising-based models remain a significant revenue driver for online entertainment services, leveraging targeted ads to generate income from user engagement. The coexistence of multiple revenue models underscores the importance for market players to diversify their monetization strategies to enhance profitability and long-term sustainability.
The segmentation by content type reveals the diverse array of offerings within the online entertainment market, with video content emerging as the dominant segment. Popular streaming platforms like YouTube, Netflix, and Amazon Prime Video have played a pivotal role in driving the demand for high-quality video content, including original series and movies that cater to a global audience. The gaming content segment is experiencing rapid growth, fueled by the burgeoning popularity of esports and mobile gaming platforms that attract a wide demographic of gamers. Additionally, live streaming content
Explore Further Details about This Research Online Entertainment Market Report https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-online-entertainment-market
Key Benefits for Industry Participants and Stakeholders: –
- Industry drivers, trends, restraints, and opportunities are covered in the study.
- Neutral perspective on the Online Entertainment Market scenario
- Recent industry growth and new developments
- Competitive landscape and strategies of key companies
- The Historical, current, and estimated Online Entertainment Market size in terms of value and size
- In-depth, comprehensive analysis and forecasting of the Online Entertainment Market
Geographically, the detailed analysis of consumption, revenue, market share and growth rate, historical data and forecast (2024-2031) of the following regions are covered in Chapters
The countries covered in the Online Entertainment Market report are U.S., Canada, Mexico, Brazil, Argentina, Rest of South America, Germany, Italy, U.K., France, Spain, Netherlands, Belgium, Switzerland, Turkey, Russia, Rest of Europe, Japan, China, India, South Korea, Australia, Singapore, Malaysia, Thailand, Indonesia, Philippines, Rest of Asia-Pacific, Saudi Arabia, U.A.E, South Africa, Egypt, Israel, and Rest of the Middle East and Africa
Detailed TOC of Online Entertainment Market Insights and Forecast to 2031
Part 01: Executive Summary
Part 02: Scope Of The Report
Part 03: Research Methodology
Part 04: Online Entertainment Market Landscape
Part 05: Pipeline Analysis
Part 06: Online Entertainment Market Sizing
Part 07: Five Forces Analysis
Part 08: Online Entertainment Market Segmentation
Part 09: Customer Landscape
Part 10: Regional Landscape
Part 11: Decision Framework
Part 12: Drivers And Challenges
Part 13: Online Entertainment Market Trends
Part 14: Vendor Landscape
Part 15: Vendor Analysis
Part 16: Appendix
Browse More Reports:
Pet Wearable Market – Industry Trends and Forecast
Food and Beverage Sterilizing Agents Market – Industry Trends and Forecast
Wireless LAN Controller Market – Industry Trends and Forecast
Refurbished Medical Imaging Equipments Market – Industry Trends and Forecast
Cell Based Assays Market – Industry Trends and Forecast
Activated Carbon Market – Industry Trends and Forecast
Edible Flakes Market – Industry Trends and Forecast
Europe Ink Resins Market – Industry Trends and Forecast
Asia-Pacific Ink Resins Market – Industry Trends and Forecast
Middle East and Africa Ink Resins Market – Industry Trends and Forecast
North America Ink Resins Market – Industry Trends and Forecast
Molded Pulp Packaging Market – Industry Trends and Forecast
Asia-Pacific Chromatography Columns Market – Industry Trends and Forecast
Europe Chromatography Columns Market – Industry Trends and Forecast
Middle East and Africa Chromatography Columns Market – Industry Trends and Forecast
Data Bridge Market Research:
Today's trends are a great way to predict future events!
Data Bridge Market Research is a market research and consulting company that stands out for its innovative and distinctive approach, as well as its unmatched resilience and integrated methods. We are dedicated to identifying the best market opportunities, and providing insightful information that will help your business thrive in the marketplace. Data Bridge offers tailored solutions to complex business challenges. This facilitates a smooth decision-making process. Data Bridge was founded in Pune in 2015. It is the product of deep wisdom and experience.
Contact Us:
Data Bridge Market Research
US: +1 614 591 3140
UK: +44 845 154 9652
APAC: +653 1251 978