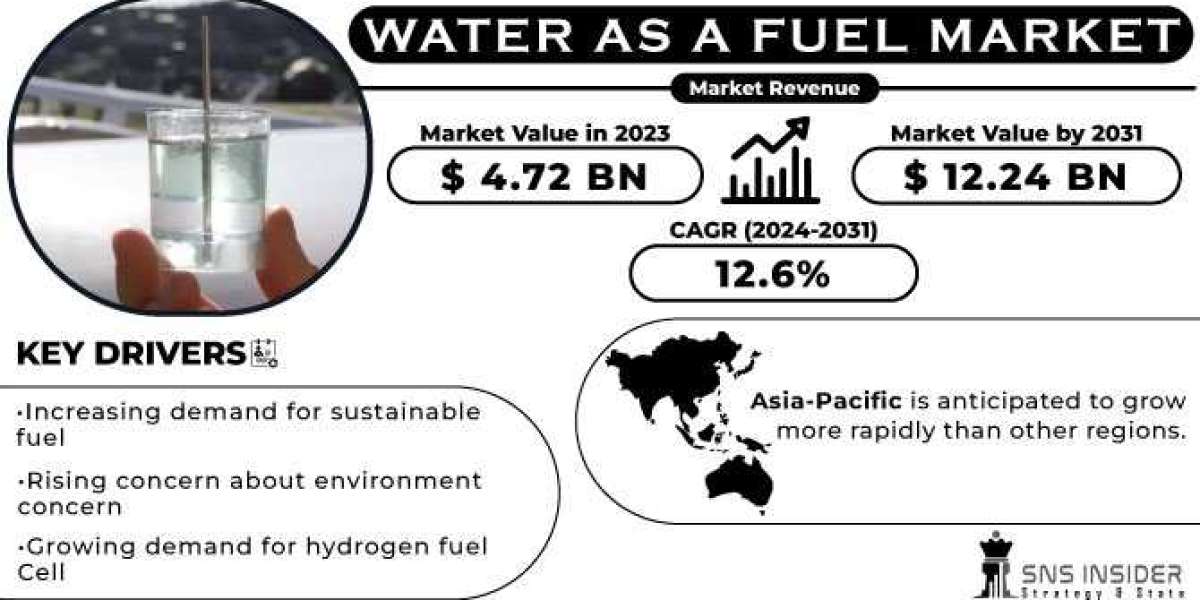
The Water as a Fuel Market size was valued at USD 4.72 billion in 2023 and is expected to grow to USD 12.24 billion by 2031 and grow at a CAGR of 12.6 % over the forecast period of 2024–2031.
The Water as a Fuel Market is emerging as a potential solution to global energy challenges, driven by the search for sustainable, eco-friendly energy sources. Water, when split into hydrogen and oxygen through processes like electrolysis, has the potential to be used as a clean energy carrier. Hydrogen, in particular, is seen as a key player in the transition toward green energy, with a focus on reducing carbon emissions and dependence on fossil fuels. The market is still in the developmental stages, but it is expected to grow rapidly in the coming years.
Market Segmentation
By Fuel Type
- Hydrogen:
- Hydrogen is the most common form of water-based fuel, produced by splitting water molecules (H2O) through electrolysis or other chemical processes. It is gaining traction in industries such as automotive (hydrogen fuel cells), energy storage, and power generation as a clean, efficient fuel.
- Oxyhydrogen:
- Oxyhydrogen is a mixture of hydrogen and oxygen gases produced through electrolysis. It is utilized as a fuel in various applications, particularly in welding, cutting, and some experimental engines. It is also being explored for its potential in high-efficiency energy systems.
By Technology
- Electrolysis:
- The most widely known and researched technology for extracting hydrogen from water. Electrolysis uses electricity to break down water into hydrogen and oxygen. The efficiency and sustainability of this method are greatly enhanced when powered by renewable energy sources, making it a key technology for the green hydrogen economy.
- Natural Gas Reforming:
- While not directly related to water splitting, natural gas reforming can be coupled with water (steam methane reforming, or SMR) to produce hydrogen. It is currently a dominant method for hydrogen production but is less sustainable than electrolysis due to associated carbon emissions. It is often seen as a transitional method until more eco-friendly technologies become cost-effective at scale.
By Region
- North America:
- The U.S. and Canada are leading the research and development of water as a fuel, particularly in hydrogen fuel cell technology. Investments in hydrogen infrastructure, such as production facilities and refueling stations, are expected to grow significantly.
- Europe:
- Europe has made significant strides in promoting water-based fuel technologies as part of its green energy transition. Countries like Germany, the UK, and France are exploring hydrogen as a key energy carrier, with policies in place to encourage production and adoption of hydrogen-based fuels.
- Asia Pacific:
- The region, particularly Japan, South Korea, and China, is making significant investments in hydrogen technology. Japan is already a leader in hydrogen fuel cell vehicles, and China is expanding its hydrogen economy, making it a key market for water as a fuel.
- Latin America:
- Latin American countries are beginning to explore water-based fuels as part of their energy transition plans. Brazil, in particular, is investing in sustainable energy solutions, including hydrogen and water-splitting technologies.
- Middle East Africa (MEA):
- The region is looking toward hydrogen as a way to diversify its energy economy, moving beyond oil and gas. Countries like Saudi Arabia and the UAE are exploring hydrogen production from water as part of their long-term sustainability strategies.
Key Market Drivers
- Sustainability and Clean Energy Initiatives:
- Increasing demand for green and renewable energy sources is driving the adoption of water as a fuel, especially hydrogen. Government incentives and global sustainability goals are accelerating the market for hydrogen and oxyhydrogen as viable alternatives to fossil fuels.
- Technological Advancements:
- Advancements in electrolysis technology, including improvements in efficiency and cost, are making water splitting more commercially viable. Innovations such as PEM (Proton Exchange Membrane) and alkaline electrolysis are gaining attention for their potential to produce high-purity hydrogen at lower costs.
- Government Policies and Support:
- Governments worldwide are implementing regulations, subsidies, and funding to support the transition to hydrogen and other water-based fuels. The EU, U.S., and Japan have made significant commitments to hydrogen production as part of their climate action strategies.
- Energy Storage and Transport:
- Hydrogen and oxyhydrogen are being increasingly recognized for their role in energy storage and transport. Hydrogen can be stored and transported efficiently, allowing it to serve as a bridge for renewable energy that can be used when production from solar or wind sources is low.
Market Challenges
- High Production Costs:
- The current cost of producing hydrogen via electrolysis remains relatively high compared to conventional fuels. However, cost reductions through technological advancements and economies of scale are expected over time.
- Infrastructure Development:
- A major hurdle to the widespread adoption of hydrogen and oxyhydrogen as fuels is the lack of refueling infrastructure, including hydrogen production plants, storage, and refueling stations.
- Efficiency and Scalability:
- While electrolysis is an eco-friendly method, it requires significant energy input. Scaling this technology to produce hydrogen at an industrial level remains a challenge, especially if the electricity used is not renewable.
Market Outlook and Forecast
The global market for water as a fuel is expected to grow rapidly from 2024 to 2031. The hydrogen economy, driven by renewable energy adoption and technological advancements, will be a key contributor. By 2030, water-based fuel technologies are expected to be integral to global efforts to achieve carbon neutrality. However, large-scale adoption will depend on overcoming challenges related to cost, infrastructure, and efficiency.
Key Forecasts:
- Hydrogen production via electrolysis will see major growth, driven by decreasing production costs and increased renewable energy integration.
- Oxyhydrogen will remain a niche market with applications in specialized industries such as welding and cutting.
- Asia-Pacific will dominate the market, with countries like Japan, South Korea, and China leading the charge in hydrogen adoption.
- North America and Europe will follow closely, supported by policy initiatives and technological advancements.
Conclusion
Water as a fuel, especially hydrogen and oxyhydrogen, holds immense potential as part of the global shift towards clean, renewable energy. The market is poised for growth, fueled by technological advancements, supportive government policies, and the rising demand for sustainable energy solutions across multiple sectors, from transportation to power generation.
Report Insights:
- Market size, growth trends, and forecasts
- Segmentation analysis by fuel type, technology, and region
- Key players and competitive landscape
- Government policies and technological developments
Read Complete Report Details of Water as a Fuel Market 2024–2031@ https://www.snsinsider.com/reports/water-as-a-fuel-market-3333
About Us:
SNS Insider is a global leader in market research and consulting, shaping the future of the industry. Our mission is to empower clients with the insights they need to thrive in dynamic environments. Utilizing advanced methodologies such as surveys, video interviews, and focus groups, we provide up-to-date, accurate market intelligence and consumer insights, ensuring you make confident, informed decisions.
Contact Us:
Akash Anand — Head of Business Development Strategy
info@snsinsider.com
Phone: +1–415–230–0044 (US) | +91–7798602273 (IND)