Eating disorders are complex mental health conditions that affect individuals both physically and emotionally.
They are not simply about food or weight but often stem from deep-seated emotional issues, trauma, societal pressures, and a range of psychological factors.
Therapy plays a crucial role in addressing these underlying issues and supporting individuals on their journey to recovery.
This article will explore the role of therapy in overcoming eating disorders, highlighting various therapeutic approaches and their benefits.
Understanding Eating Disorders
Before delving into the role of therapy, it’s important to understand the nature of eating disorders.
Common eating disorders include anorexia nervosa, bulimia nervosa, and binge-eating disorder.
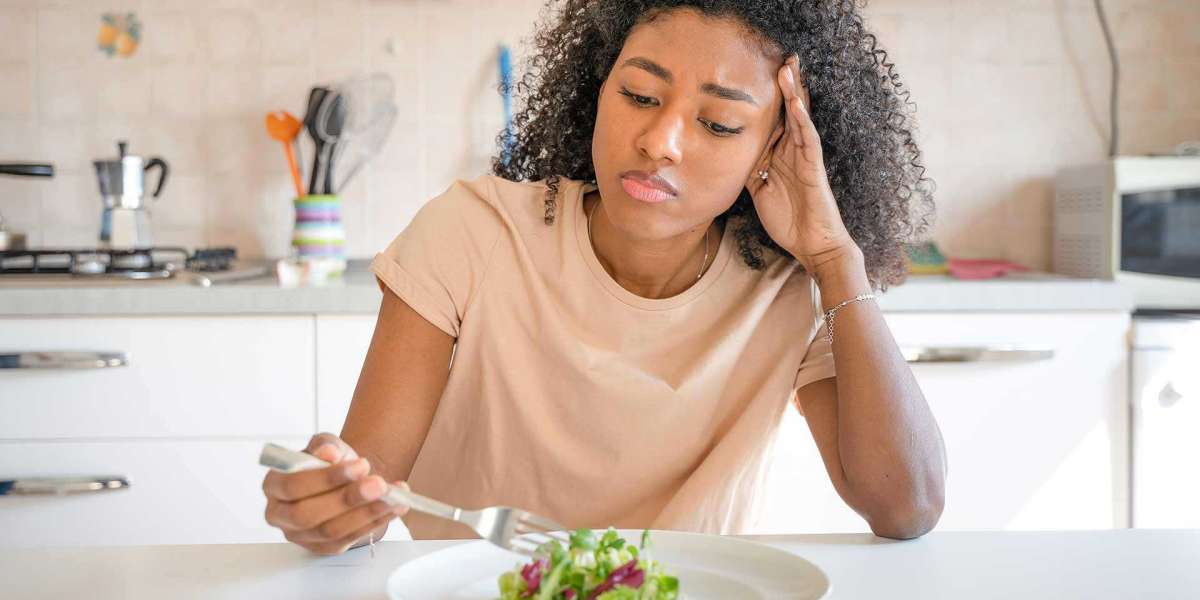
These conditions are characterized by unhealthy eating behaviors and an intense preoccupation with food, weight, and body image. Eating disorders can lead to serious physical health issues, including heart problems, malnutrition, and even death.
However, the emotional toll is equally significant, as those suffering often experience shame, guilt, depression, and anxiety.
Eating disorders are not simply about control over food; they are often a manifestation of deeper psychological distress.
Therapy is essential because it helps individuals confront the underlying emotional and mental health issues driving these behaviors.
Types of Therapy Used in Eating Disorder Treatment
There is no one-size-fits-all approach to treating eating disorders, and therapy is often tailored to the specific needs of the individual.
However, there are several evidence-based therapeutic approaches that have been proven effective in treating these conditions.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is one of the most common therapeutic approaches used to treat eating disorders.
CBT focuses on identifying and challenging the negative thought patterns and beliefs that contribute to disordered eating behaviors.
For example, someone with anorexia may have a distorted perception of their body size, while someone with bulimia may feel that purging is the only way to control their weight.
CBT helps individuals reframe these negative thoughts and develop healthier coping mechanisms.
By addressing the thought patterns behind disordered eating behaviors, CBT can lead to lasting change. Many individuals find that through this therapy, they are able to break free from destructive cycles and develop a healthier relationship with food and their body.
Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT)
Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) is another therapeutic approach that has proven effective for those struggling with eating disorders, particularly for individuals with bulimia and binge-eating disorder.
DBT focuses on teaching skills for emotional regulation, distress tolerance, and mindfulness.
Eating disorders are often linked to difficulty managing emotions, and DBT provides individuals with tools to handle these intense feelings in healthier ways.
By learning to regulate emotions and tolerate distress without resorting to harmful behaviors, individuals can build resilience and avoid relapse.
DBT also emphasizes the importance of mindfulness, helping individuals stay present and develop greater self-awareness.
Family-Based Therapy (FBT)
For adolescents and young adults with eating disorders, Family-Based Therapy (FBT) is a highly effective treatment approach.
Eating disorders can disrupt family dynamics, and FBT involves the family in the recovery process.
Parents and other family members are taught how to support their loved one in a healthy way, helping them regain control of their eating patterns.
FBT is particularly effective for younger individuals because it recognizes the importance of a supportive home environment.
Families learn to avoid enabling behaviors and instead create a structure that promotes recovery. This approach fosters open communication and healing within the family unit.
Psychodynamic Therapy
Psychodynamic therapy focuses on exploring the unconscious thoughts, feelings, and experiences that may have contributed to the development of an eating disorder.
This type of therapy is beneficial for individuals who may have experienced trauma or unresolved emotional issues that are driving their disordered eating behaviors.
By uncovering these unconscious factors, individuals can gain insight into their emotional struggles and work through them in a supportive therapeutic environment.
This approach can be especially helpful for individuals who have not responded well to more structured therapies like CBT or DBT.
The Benefits of Therapy in Eating Disorder Recovery
Therapy is not a quick fix for eating disorders; recovery is often a long-term process that requires commitment and patience.
However, therapy offers several key benefits that are crucial to overcoming these conditions.
1. Addressing the Root Causes
Therapy goes beyond addressing the symptoms of eating disorders and works to identify the root causes.
Whether it’s trauma, low self-esteem, or societal pressures, therapy helps individuals confront the issues that led to the development of their eating disorder.
2. Developing Coping Strategies
Many individuals with eating disorders use disordered eating behaviors as a way to cope with overwhelming emotions.
Therapy teaches individuals healthier coping strategies, enabling them to manage stress, anxiety, and depression without resorting to harmful behaviors.
3. Building a Support System
A strong support system is essential for recovery, and therapy provides individuals with a safe space to express their emotions without judgment.
Group therapy, in particular, can be a valuable tool for connecting with others who are going through similar experiences, providing both accountability and encouragement.
4. Preventing Relapse
Eating disorders are chronic conditions, and the risk of relapse is always present.
Therapy helps individuals develop the skills they need to maintain recovery in the long term.
By addressing both the emotional and behavioral aspects of eating disorders, therapy reduces the risk of relapse and promotes lasting healing.
Conclusion
The role of therapy in overcoming eating disorders cannot be overstated.
By addressing the underlying emotional and psychological issues that drive disordered eating behaviors, therapy provides individuals with the tools they need to heal and recover.
Whether through CBT, DBT, or family-based therapy, the therapeutic process empowers individuals to regain control over their lives and develop a healthier relationship with food and their bodies.
Overcoming an eating disorder is a journey, but with the right therapeutic support, lasting recovery is possible.