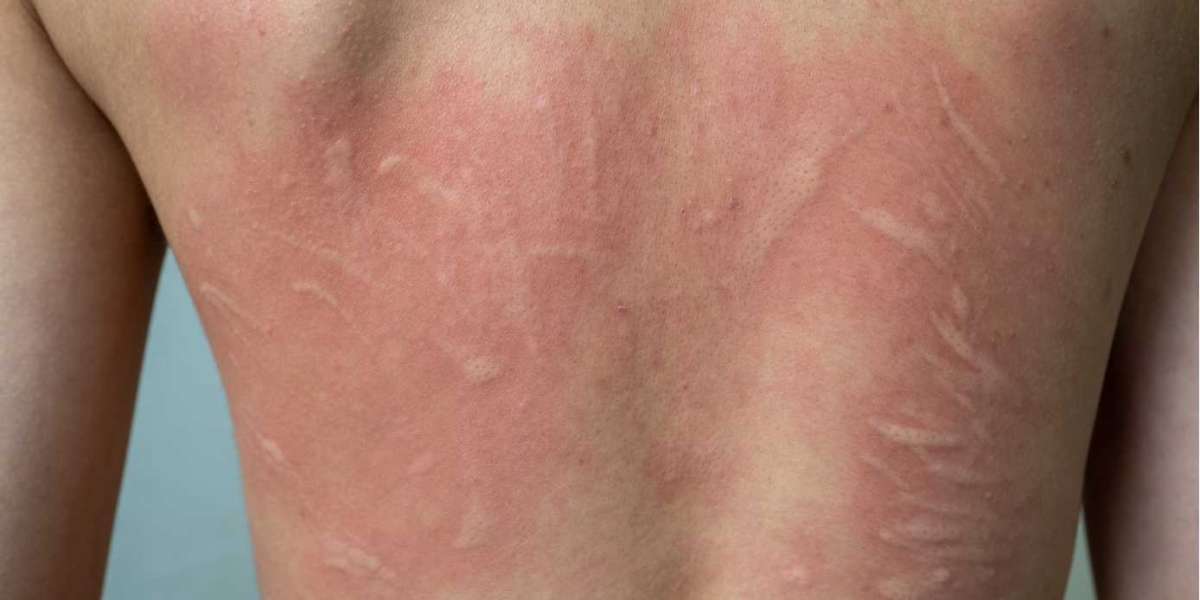
Urticaria, commonly known as hives, is a skin condition characterized by raised, itchy welts that can appear suddenly and vary in size and shape. These welts may be triggered by allergens, stress, infections, or medications, though the cause is often unidentified. While urticaria is typically not life-threatening, its impact on quality of life (QoL) is profound, affecting physical, emotional, and social well-being. This article explores how urticaria influences daily life, the challenges patients face, and the role of treatments, including those supplied by cephalexin suppliers, in managing symptoms.
Physical Impact of Urticaria
The most immediate effect of urticaria is physical discomfort. The intense itching, burning, or stinging sensations can disrupt sleep, leading to fatigue and reduced daytime productivity. For individuals with chronic urticaria defined as symptoms persisting for six weeks or longer these disturbances become a persistent burden. Studies indicate that up to 50% of patients with chronic urticaria experience sleep disturbances, which exacerbate other health issues like anxiety and weakened immune function.
Beyond itching, urticaria can cause swelling (angioedema), particularly in sensitive areas like the face, lips, or throat. This swelling can be painful and, in severe cases, interfere with breathing or swallowing, necessitating urgent medical attention. The unpredictability of flare-ups adds to the physical toll, as patients may need to avoid certain foods, environments, or activities to prevent episodes. For example, those with urticaria triggered by infections may require antibiotics from reliable cephalexin suppliers to address underlying bacterial causes, such as streptococcal infections, which are known to precipitate hives in some cases.
The physical appearance of hives also affects QoL. Welts can be unsightly, leading patients to cover affected areas or avoid public settings. This is particularly challenging for individuals whose urticaria affects visible areas like the face or hands, as it can lead to self-consciousness and reduced participation in professional or recreational activities.
Emotional and Psychological Effects
The emotional burden of urticaria is significant. The chronic nature of the condition, coupled with its unpredictability, fosters anxiety and frustration. Patients often live in fear of the next flare-up, which can occur without warning. This constant vigilance can lead to stress, which, ironically, is a known trigger for urticaria, creating a vicious cycle. Research shows that approximately 30% of patients with chronic urticaria report symptoms of anxiety, while 15% experience depression linked to their condition.
The stigma associated with visible skin conditions further compounds emotional distress. Patients may feel embarrassed or judged, particularly if others mistakenly believe urticaria is contagious. This misconception can lead to social isolation, as individuals withdraw to avoid scrutiny or questions. For children and adolescents with urticaria, bullying or teasing can exacerbate feelings of inadequacy, impacting self-esteem and academic performance.
Moreover, the reliance on medications to manage symptoms can be emotionally taxing. While antihistamines are the first-line treatment for urticaria, some patients require additional therapies, such as antibiotics from cephalexin suppliers for infection-related triggers or corticosteroids for severe cases. The need for ongoing medication, potential side effects, and varying efficacy can lead to feelings of helplessness, particularly when treatments fail to provide consistent relief.
Social and Occupational Challenges
Urticaria’s impact extends to social interactions and professional life. The condition can limit participation in social activities, such as dining out or attending events, due to dietary restrictions or fear of environmental triggers. For instance, patients with cold urticaria, a subtype triggered by low temperatures, may avoid outdoor activities in cooler climates, reducing their ability to engage with friends or family.
In the workplace, urticaria can hinder performance and career progression. Frequent absences due to flare-ups or doctor’s appointments disrupt work schedules, while symptoms like itching or fatigue impair concentration and productivity. Visible hives may also affect professional confidence, particularly in roles requiring public interaction. A 2018 study found that 20% of patients with chronic urticaria reported reduced work efficiency, and some faced job loss due to their condition.
The financial burden of managing urticaria adds another layer of strain. Costs associated with doctor visits, medications, and specialized products (e.g., hypoallergenic clothing) can accumulate quickly. For patients requiring antibiotics from cephalexin suppliers to treat infection-related urticaria, the expense of ongoing prescriptions can be significant, especially in regions with limited healthcare coverage.
Treatment and Management Strategies
Effective management of urticaria is critical to improving QoL. The cornerstone of treatment is identifying and avoiding triggers, though this is challenging when causes are idiopathic. Antihistamines, both sedating and non-sedating, are widely used to control itching and reduce welts. However, for patients with infection-triggered urticaria, antibiotics like cephalexin, sourced from reputable cephalexin suppliers, may be prescribed to address underlying bacterial infections. Cephalexin, a first-generation cephalosporin, is effective against common pathogens like Staphylococcus aureus, which can exacerbate urticaria in some cases.
For severe or refractory cases, additional therapies such as omalizumab (an anti-IgE monoclonal antibody) or immunosuppressive drugs may be considered. These treatments, while effective, are costly and may not be accessible to all patients. Lifestyle modifications, such as stress management techniques and dietary changes, also play a role in reducing flare-ups. Patients are often advised to keep a symptom diary to identify patterns and triggers, which can guide treatment plans.
Education and support are equally important. Patient advocacy groups and online communities provide resources and emotional support, helping individuals cope with the psychological and social challenges of urticaria. Healthcare providers can further improve QoL by offering empathetic care and personalized treatment plans, ensuring patients feel heard and understood.
The Role of Cephalexin in Urticaria Management
While cephalexin is not a primary treatment for urticaria, its role in managing infection-related cases is noteworthy. Bacterial infections, particularly those caused by Streptococcus or Staphylococcus species, can trigger or worsen urticaria in some patients. Cephalexin, supplied by trusted cephalexin suppliers, targets these pathogens, reducing the inflammatory response that contributes to hive formation. By addressing the root cause, cephalexin can help prevent recurrent flare-ups, thereby improving QoL for affected individuals.
However, the use of cephalexin must be carefully monitored, as inappropriate antibiotic use can lead to resistance or side effects like gastrointestinal upset. Physicians typically prescribe cephalexin only when a bacterial infection is confirmed or strongly suspected, ensuring its benefits outweigh potential risks.
Conclusion
Urticaria is far more than a skin condition; it is a chronic illness that disrupts physical comfort, emotional well-being, and social functioning. The constant threat of flare-ups, coupled with the challenges of managing symptoms, takes a significant toll on quality of life. While treatments like antihistamines and antibiotics from cephalexin suppliers offer relief for some, the condition’s unpredictability and psychological impact require a holistic approach to care.