Here’s a comprehensive 2000-word article on "Combating High Prolactin: Cabergoline for Bone Health, Menstrual Regularity, and Fertility."
Introduction
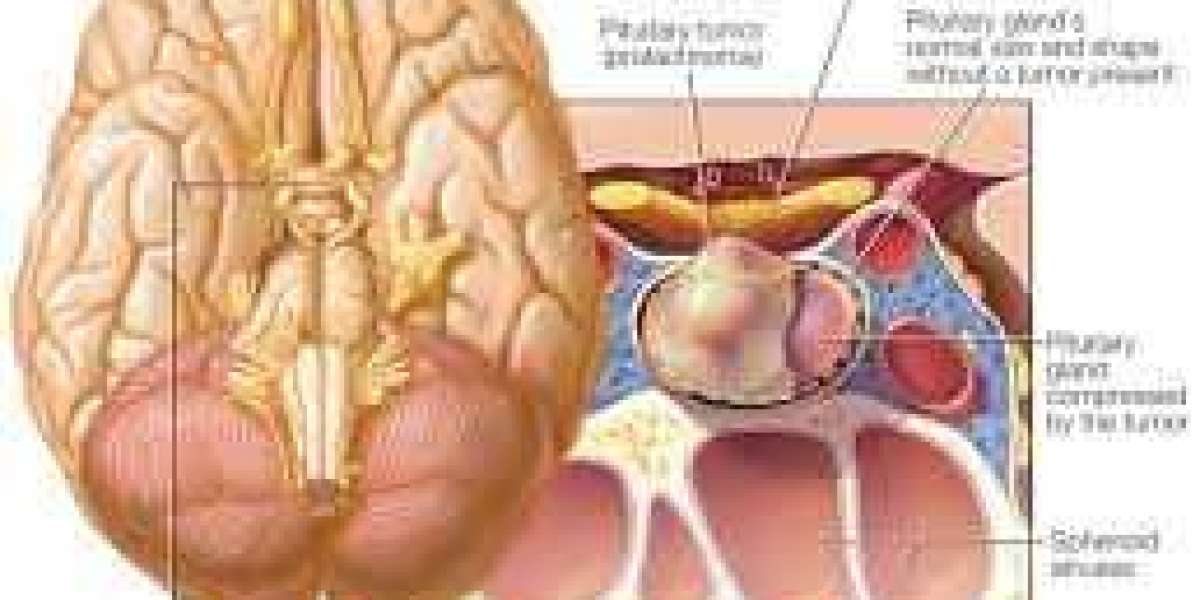
High prolactin levels, a condition known as hyperprolactinemia, can lead to a range of health concerns, especially in reproductive health, menstrual cycles, and bone density. When prolactin levels rise beyond normal, it can disrupt menstrual cycles, cause infertility, and increase the risk of osteoporosis due to decreased bone mineral density. One of the most effective treatments for managing hyperprolactinemia is Cabergoline 0.5 mg and Cabergoline 0.25 mg doses.
Cabergoline works by inhibiting prolactin secretion from the pituitary gland, making it a preferred treatment option for patients dealing with high prolactin levels. This article will explore how Cabergoline helps manage prolactin levels, its benefits for bone health, menstrual regularity, and fertility, and the significance of its two doses—0.5 mg and 0.25 mg.
Understanding Prolactin and Hyperprolactinemia
Prolactin is a hormone produced by the pituitary gland, primarily known for its role in stimulating breast milk production after childbirth. Besides lactation, prolactin influences reproductive health, immune response, and metabolism. However, excessive prolactin secretion, or hyperprolactinemia, can disrupt these bodily functions.
Hyperprolactinemia often results from:
- Pituitary tumors (prolactinomas)
- Certain medications
- Hypothyroidism
- Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS)
Increased prolactin levels in women can lead to irregular periods, amenorrhea (absence of menstruation), and anovulation (failure to release eggs), while men might experience reduced libido and fertility issues. For both genders, high prolactin levels can lead to low bone density and an increased risk of osteoporosis.
Cabergoline as a Treatment for High Prolactin
Cabergoline, a dopamine agonist, is specifically designed to reduce prolactin production in the pituitary gland. Dopamine, a neurotransmitter, acts as a natural inhibitor of prolactin, and Cabergoline mimics dopamine's action by binding to dopamine receptors, thereby inhibiting prolactin release.
Cabergoline is available in 0.5 mg and 0.25 mg doses. It is usually taken orally, with dosing frequency depending on the patient's initial prolactin level and response to treatment. Typically, doctors start with a low dose and gradually adjust it to find the optimal therapeutic level.
Mechanism of Action of Cabergoline
Cabergoline selectively targets dopamine D2 receptors, primarily located in the anterior pituitary gland. By binding to these receptors, Cabergoline inhibits prolactin secretion from lactotroph cells in the pituitary. The drug's long half-life allows it to suppress prolactin effectively for an extended period, enabling patients to take it just once or twice a week, enhancing patient compliance and convenience.
Benefits of Cabergoline for Bone Health
One often overlooked consequence of high prolactin levels is bone density loss. Prolactin interferes with estrogen levels in women and testosterone levels in men, hormones essential for maintaining healthy bones. In women, estrogen plays a vital role in promoting calcium absorption and deposition into bones, while testosterone in men stimulates bone formation.
When prolactin levels remain elevated, estrogen and testosterone levels fall, accelerating bone loss. This bone demineralization can lead to osteopenia (reduced bone density) and, over time, osteoporosis, where bones become fragile and more susceptible to fractures.
Cabergoline helps mitigate this risk by restoring prolactin levels to normal, allowing the body to maintain healthy estrogen and testosterone levels. Consequently, the use of caffeine contributes to improved bone mineral density, especially in women with amenorrhea due to hyperprolactinemia. Studies have shown that long-term treatment with cabergoline can result in significant improvements in bone density, reducing the risk of osteoporosis and associated complications.
Enhancing Menstrual Regularity and Reproductive Health
Menstrual irregularities are one of the most common symptoms of hyperprolactinemia. Elevated prolactin levels disrupt the production of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH), which plays a critical role in regulating the menstrual cycle and ovulation. This interference can lead to irregular cycles, anovulation, or amenorrhea, significantly impacting fertility.
Cabergoline, by lowering prolactin levels, can restore regular menstrual cycles in women with hyperprolactinemia. As prolactin levels normalize, the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis is restored, allowing for regular GnRH secretion and subsequent follicular development and ovulation. This regularization of menstrual cycles not only improves reproductive health but also addresses symptoms like breast tenderness and mood swings often associated with high prolactin levels.
For women trying to conceive, Cabergoline's impact on menstrual regularity and ovulation can significantly enhance fertility. Restoring ovulatory cycles increases the chances of conception, making Cabergoline a valuable treatment option for women with hyperprolactinemia-related infertility. Studies have demonstrated that Cabergoline effectively induces ovulation and restores fertility in many women with prolactinomas, especially those with mild-to-moderate prolactin elevations.
Cabergoline and Male Fertility
While hyperprolactinemia predominantly affects women, it can also impact men's health, especially reproductive function. High prolactin levels in men are associated with decreased testosterone production, resulting in reduced libido, erectile dysfunction, and sometimes infertility.
Cabergoline treatment in men can help restore testosterone levels by lowering prolactin, subsequently improving libido and enhancing fertility potential. Additionally, lowering prolactin levels may improve sperm production, leading to better sperm quality and count.
Dosage Considerations: Cabergoline 0.5 mg vs. 0.25 mg
Cabergoline is commonly prescribed in 0.5 mg and 0.25 mg doses, depending on the severity of hyperprolactinemia and the patient's response. A low starting dose is generally recommended to minimize potential side effects.
- Cabergoline 0.25 mg: This is the lowest available dose and is often used at the start of treatment or for patients who are particularly sensitive to medication. It's typically administered once or twice per week.
- Cabergoline 0.5 mg: The 0.5 mg dose is usually prescribed for individuals who require a higher dose to effectively lower their prolactin levels. Some patients may require multiple doses per week, although once-a-week dosing is generally effective due to cabergoline’s long half-life.
Doctors frequently tailor the dosage regimen to achieve a gradual reduction in prolactin levels, assessing serum prolactin levels periodically to avoid over-suppression, which could lead to potential side effects.
Potential Side Effects of Cabergoline
While cabergoline is highly effective, it is essential to consider potential side effects, which may include:
- Nausea and vomiting: common in the early stages of treatment but usually subsides with time.
- Dizziness and Headaches: Due to its dopamine agonist activity, cabergoline can cause dizziness, especially when standing up suddenly.
- Fatigue: Some patients may feel unusually tired, especially in the initial days of treatment.
- Orthostatic Hypotension: A drop in blood pressure upon standing can occur, especially when the drug is first started.
- Cardiac Valve Fibrosis: This rare but serious side effect is associated with long-term use of Cabergoline. Regular echocardiograms are recommended for those on prolonged treatment.
Patients are encouraged to follow their healthcare provider’s instructions closely and report any unusual symptoms. Most side effects are manageable with appropriate medical guidance, and Cabergoline's benefits often outweigh these risks for those with high prolactin levels.
Monitoring Prolactin Levels During Treatment
It is essential to monitor prolactin levels regularly to assess the effectiveness of Cabergoline and adjust the dose if necessary. Doctors usually recommend a follow-up prolactin test within 2-4 weeks after initiating Cabergoline therapy and periodic testing every few months thereafter. Once prolactin levels normalize, dosing frequency may be adjusted, or the drug may be tapered to the lowest effective dose to maintain prolactin suppression.
In cases of prolactinoma, MRI scans may also be advised to monitor the tumor size, especially in patients with large pituitary adenomas.
Lifestyle Considerations Alongside Cabergoline Therapy
While cabergoline is highly effective, incorporating healthy lifestyle habits can support treatment outcomes.
- Calcium and Vitamin D Intake: Ensuring adequate calcium and vitamin D is crucial for bone health, especially in individuals at risk of osteoporosis.
- Regular Exercise: Weight-bearing exercises strengthen bones, enhancing bone mineral density.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can exacerbate hormone imbalances, making stress management techniques beneficial.
- Dietary Choices: A balanced diet rich in nutrients can aid hormonal balance and overall health.
Conclusion
Cabergoline has transformed the management of high plasma levels, providing a reliable solution for patients with hyperprolactinemia. By lowering prolactin levels, cabergoline restores menstrual regularity, enhances fertility, and helps maintain bone health in both men and women. Its convenience of dosing (0.5 mg and 0.25 mg options) allows for individualized treatment plans, making it accessible to a broad range of patients.
If you or someone you know is dealing with high prolactin levels, discussing cabergoline with a healthcare provider can provide an effective path to symptom relief and improved quality of life. Managing prolactin levels is not just about addressing hormonal imbalance; it’s about restoring a sense of well-being, health, and vitality.