Cryo Electron Microscopy
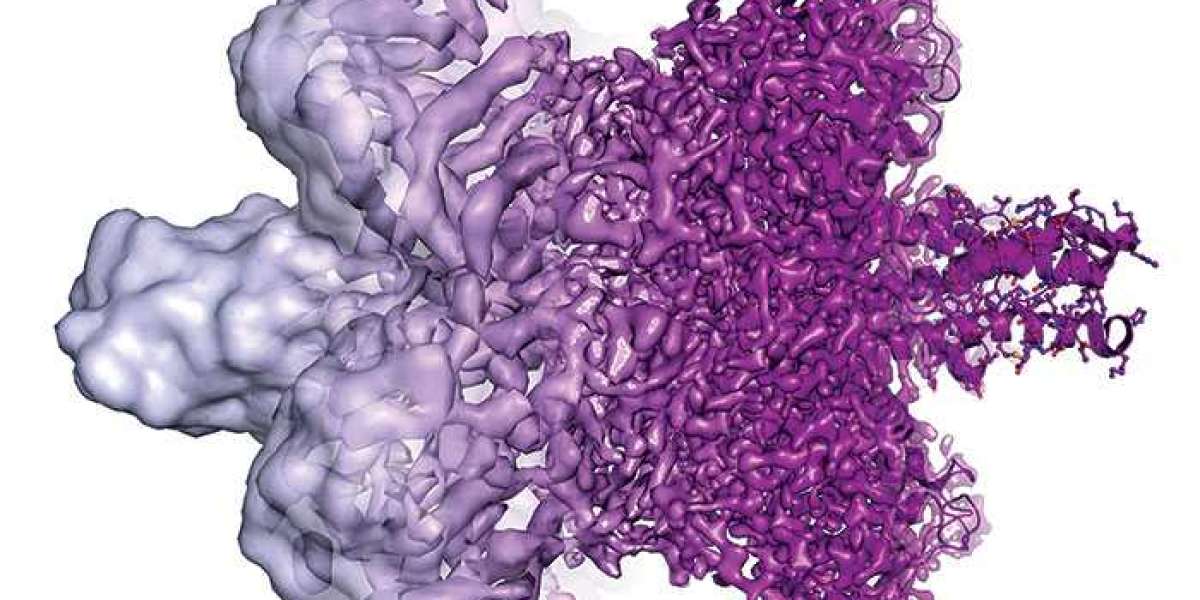
Cryo electron microscopy (cryo-EM) is a technique used to view biological samples at atomic resolution by flash-freezing them and imaging their structure with electron microscopes. While electron microscopes have been used in research since the 1930s, recent advances in detector and microscope technology have enabled cryo-EM to achieve "atomic resolution" below 4 angstroms—making it possible to visualize individual atoms. This breakthrough has revolutionized structural biology and is transforming drug discovery.
Detector Technology Advances Enable Higher Resolution Imaging
One of the major factors enabling high-resolution Cryo Electron Microscopy imaging has been improvements in direct electron detectors. Older photographic film and CCD camera detectors captured low signal and had low sensitivity, making high-resolution imaging difficult. New direct electron detectors like silicon pixel array detectors provide much higher detective quantum efficiency and faster readout speeds. They can capture many more electrons from each exposure, yielding images with higher signal-to-noise ratios. This allows reconstruction of finer structural details from a sample. The latest generation of direct detectors has ushered cryo-EM into the "atomic resolution" era below 4 angstroms.
Higher Magnetic Fields and Corrector Lenses Boost Resolution
Another key development has been the of higher voltage transmission electron microscopes equipped with spherical aberration corrector lenses. Operating electrons industry overview at 300kV rather than the traditional 120kV provides improved resolution. And corrector lenses counteract inherent "spherical aberration" from an electron microscope's objective lens, sharpening the focus of the imaged beam. Together, higher voltages and correctors increase the "information limit" or resolution ceiling of electron microscopes. The highest-end microscopes now routinely image below 4 angstrom resolution.
Get More Insights On- Cryo Electron Microscopy