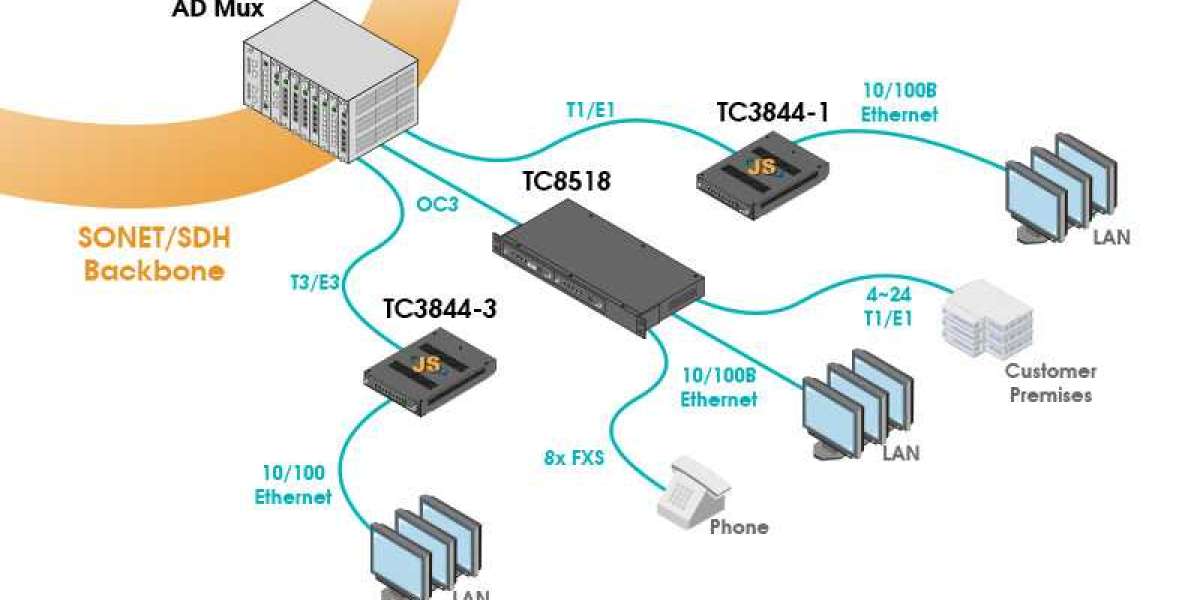
Synchronous Optical Network, commonly known as SONET, is a standardized protocol that transmits digital signals over optical fiber using lasers or LEDs. SONET was originally designed to transport circuit encoded T1/E1 signals over fiber as it provides robust error correction techniques to transmit voice, data and video digitally and reliably over long distances.
SONET Frame Structure
At the core of SONET is its frame structure which is made up of 810 bytes of data including control information that is transmitted every 125 microseconds, known as a SONET frame. The basic building block of a SONET frame is 90 bytes which repeats 8 times to form the full frame of 810 bytes. This frame structure provides flexibility in transporting different line rates using multiplexing. The most common SONET rates are OC-1, OC-3, OC-12, OC-48 and OC-192.
Data Encoding in SONET
To transmit the digital data over fiber, Synchronous Optical Network uses a technique called Synchronous Transport Signal (STS). The STS frame contains the SONET overhead and payload. The overhead contains framing, timing and error correction bits while the payload area transports the customer data. Before transmission, the data in the STS frame is encoded using bipolar encoding to make the signal suitable for fiber transmission. This encoding scheme balances the average power of the signal and avoids long strings of consecutive 1s or 0s.
Multiplexing and Link Capacity
SONET uses multiplexing to efficiently utilize the fiber capacity. Lower rate signals like OC-1, OC-3 etc. can be combined together to create higher rate links like OC-12. This statistical multiplexing allows the bandwidth to be dynamically allocated based on the real time traffic. The basic building block is OC-1 with 51.84 Mbps capacity but networks typically use OC-3 at 155.52 Mbps as the lowest rate. The highest common rates are OC-48 and OC-192 with 2.5 Gbps and 10 Gbps capacity respectively.
Get more insights on - Synchronous Optical Network
Get More Insights—Access the Report in the Language that Resonates with You.