Tuberculosis (TB) is a disease that often conjures up images of coughing adults in overcrowded, poorly ventilated areas. However, TB is not exclusive to adults. Children can also be affected by this serious and potentially life-threatening disease, and in fact, TB in children often presents in ways that are quite different from those seen in adults. Unlike the more obvious symptoms of TB disease in adults, such as prolonged coughing and chest pain, the signs of TB in children can sometimes be more subtle, making it harder for parents to recognise the illness in its early stages. Understanding the TB symptoms in children is crucial for timely intervention, which is vital to prevent serious health complications and to avoid the spread of the disease.
In this article, we will dive deep into the symptoms of TB disease in children, providing you with key indicators to look out for. Additionally, we will discuss why it is important to have the best health insurance policy in place to ensure your child has access to the medical care they need should TB be suspected. With proper treatment, children with TB can make a full recovery, so it’s critical that parents and caregivers are well-informed.
Understanding Tuberculosis in Children
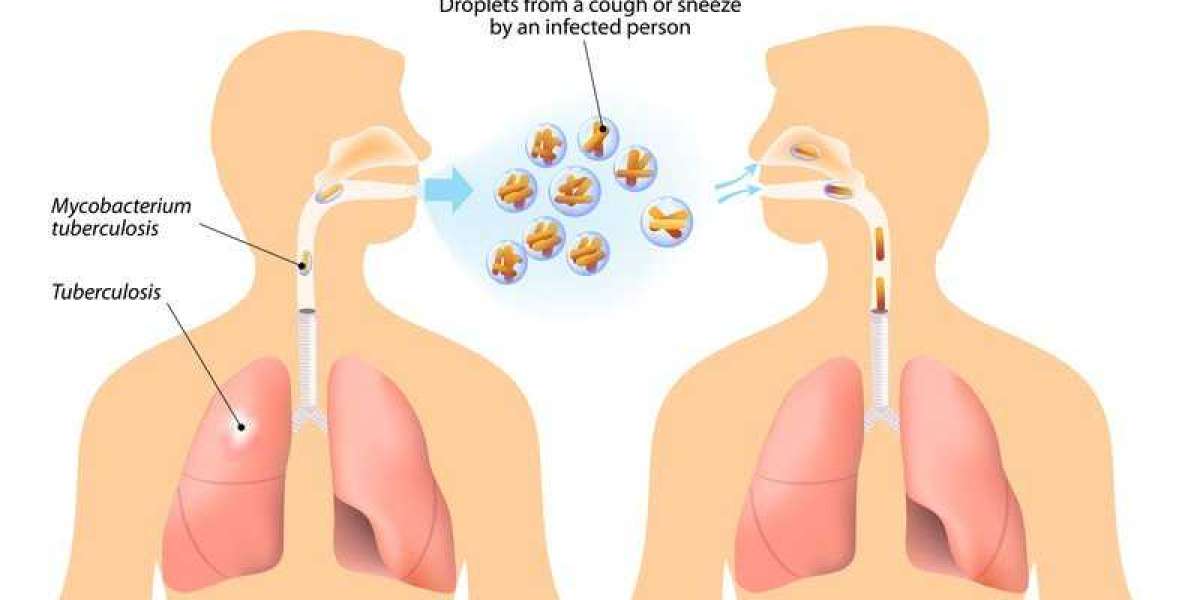
Tuberculosis is caused by the Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacteria and typically affects the lungs, although it can also spread to other parts of the body, including the brain, spine, and kidneys. In children, TB is often contracted through close contact with an infected individual, usually within the family or community. It’s important to note that children under the age of five, and those with weakened immune systems (such as those living with HIV or malnutrition), are at a higher risk for developing severe forms of TB.
When it comes to TB symptoms in children, the condition may not always manifest in the same way as it does in adults. In many cases, children may exhibit mild or non-specific symptoms, making the disease harder to detect. This is why parents and caregivers must be vigilant, especially if there is a known history of TB exposure within the household or community.
Key Symptoms of TB Disease in Children
Persistent Cough
One of the most common symptoms of TB disease in children is a persistent cough that lasts for more than three weeks. Like adults, children with TB may develop a dry cough in the early stages, but as the disease progresses, it may become productive, producing mucus or phlegm. If your child has a cough that doesn’t improve or gets worse over time, it could be a sign of TB. Parents should be especially concerned if the cough is accompanied by other symptoms such as fever or weight loss.
It’s important to note that children with TB may also experience chest pain, although this is less commonly reported in younger children compared to adults. In infants and very young children, they may not be able to communicate this symptom clearly, but signs like irritability or difficulty breathing could be warning signs.
Fever and Night Sweats
Fever is another tell-tale sign of TB in children. The fever associated with TB is often low-grade, but it can spike during the evening hours, leading to night sweats. In fact, night sweats can be one of the most distinctive symptoms, as the fever typically subsides during the day, but reappears at night, causing the child to sweat heavily, even soaking through their pajamas or bedding
Persistent fevers, especially when combined with other symptoms such as a cough and weight loss, should prompt parents to seek medical attention. Although fever can be caused by many illnesses, when it persists over time or is associated with other TB symptoms, it raises suspicion for TB disease.
Unexplained Weight Loss and Poor Appetite
Another key symptom of TB in children is unexplained weight loss. Children with TB often experience a loss of appetite, which leads to a gradual reduction in their overall body weight. This weight loss is often accompanied by fatigue and a general sense of being unwell. In some cases, children may appear pale or have noticeable changes in their appearance as a result of nutritional deficiencies or the body's fight against the infection.
In younger children or infants, weight loss may be harder to notice at first, but parents can track their child’s growth by comparing their weight with previous records. If your child isn’t gaining weight as expected, or if they begin to lose weight, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare provider.
Lethargy and Fatigue
Children with TB often experience a marked decrease in energy levels. They may appear more tired than usual, have trouble keeping up with their daily activities, and may be more prone to irritability or mood changes. Fatigue is a common response to any infection, but in the case of TB, it can be especially pronounced.
In babies and younger children, lethargy may be evident if they are less playful or refuse to engage in their usual activities. In older children, complaints of feeling unusually tired or needing more sleep can signal that something isn’t right.
Difficulty Breathing and Chest Pain
While rare, some children may experience difficulty breathing or chest pain if the TB infection progresses to the lungs or other organs. Difficulty breathing can be particularly concerning in young children and infants, as they may not be able to verbalise their distress. In these cases, parents may notice laboured breathing, fast or shallow breaths, or the child appearing out of breath even after minimal exertion.
Swollen Lymph Nodes
In addition to respiratory symptoms, TB can sometimes cause swelling of the lymph nodes. If your child has swollen glands in the neck or other areas that don't go away, it may be indicative of TB, especially if other symptoms are present. Swollen lymph nodes are often a sign that the body is fighting an infection, but persistent swelling should be evaluated by a doctor.
Why Does Early Detection and Treatment Matter?
Detecting TB in children early is crucial for several reasons.
- The earlier the disease is diagnosed, the sooner treatment can begin, reducing the risk of severe complications.
- Treatment for TB typically involves a long course of antibiotics, which can last from six to twelve months, depending on the severity of the disease.
- In children, timely treatment can prevent the spread of the disease to others, especially since children with TB are more likely to develop a more severe form of the disease if left untreated.
- Early intervention also improves the chances of a full recovery, so ensuring that your child has access to appropriate healthcare as soon as symptoms appear is paramount.
The Role of Health Insurance in Managing TB
A critical factor in managing TB, or any serious health condition, is access to quality healthcare. This is where the importance of having the best health insurance policy becomes clear. Medical expenses related to TB diagnosis and treatment can quickly accumulate, especially if your child requires specialised care or hospitalisation.
Having the best medical insurance policy for family coverage ensures that you have access to the necessary healthcare services, including diagnostic tests, medications, and specialist consultations. With comprehensive coverage, you can minimise the financial burden of TB treatment and focus on your child’s recovery.
When considering the best health insurance policy for your family, look for options that offer extensive coverage for infectious diseases like TB. Niva Bupa is committed to offer the best medical insurance policy for family coverage, helping you protect your loved ones from a wide range of health risks. Your child’s health is invaluable, and with Niva Bupa, you can ensure they have access to the best care possible.