Foam Insulation: Types, Benefits, and Uses for Thermal and Water Insulation
Introduction
With the advancement of building and construction technologies, thermal and water insulation have become essential elements that contribute to improving building efficiency and reducing energy consumption. Among the common types of insulation, foam insulation is one of the most effective solutions due to its high resistance to heat and moisture. Foam is used in many applications, from insulating roofs and walls to insulating tanks and pipes, making it an ideal choice for many residential, commercial, and industrial projects. In this article, we will discuss the concept of foam insulation, its types, benefits, and uses, in addition to its application method and the most important factors to consider when choosing it.
What is foam insulation?
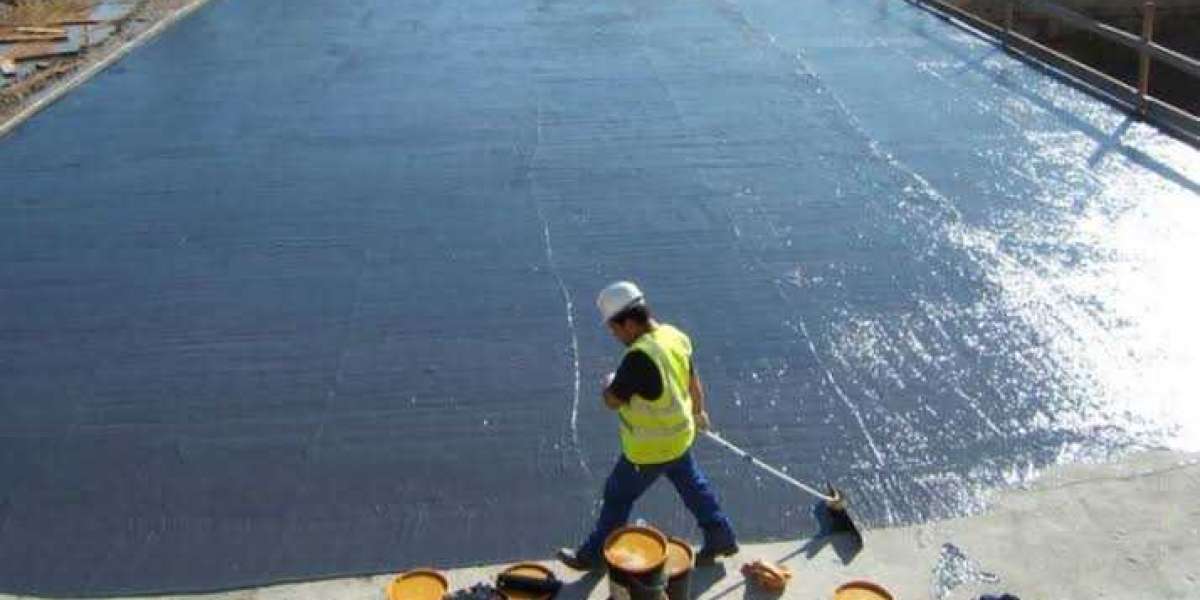
Foam insulation is a type of insulation used to protect buildings and surfaces from heat, cold, and moisture. It consists of lightweight foam materials with effective insulating properties, preventing heat leakage and maintaining a stable temperature inside the building. Foam insulation is characterized by its ability to penetrate cracks and pores, providing comprehensive protection and a tight seal against air and water leakage.
Types of Foam Insulation
There are several types of foam used for insulation, each with its own distinct properties and uses. The most prominent are:
1. Polyurethane Foam
This is one of the most popular types of foam used for thermal and water insulation.
It is characterized by its light weight and high effectiveness in preventing heat transfer.
It is available in the form of a spray foam that expands to fill gaps and cracks.
It is used for insulating roofs and walls, as well as for insulating pipes and tanks.
2. Polyethylene Foam
It is characterized by its ability to absorb shock and provide excellent sound and heat insulation.
It is primarily used for insulating pipes and building floors.
It is available in the form of flexible sheets or rolls for various uses.
3. Polystyrene Foam
There are two main types:
Expanded Polystyrene (EPS):
It is characterized by its light and flexible composition.
It is used for insulating walls and roofs. Extruded Polystyrene (XPS):
Denser and more effective at thermal insulation than EPS.
It is highly resistant to moisture, making it ideal for insulating foundations and exterior walls.
4. Spray Foam Insulation
Applied to surfaces using a special spray machine.
It expands to form a cohesive insulating layer with no joints.
It provides high resistance to heat and moisture, preventing air and water leakage.
Benefits of Foam Insulation
1. High thermal insulation efficiency
Reduces heat transfer, helping maintain stable indoor temperatures.
Leads to reduced air conditioning and heating consumption, thus reducing energy costs.
2. High resistance to moisture and water leakage
Prevents water and moisture from seeping into surfaces and walls, protecting buildings from weather damage.
Reduces the risk of mold and fungal growth.
3. Sealing Gaps and Cracks
Foam is characterized by its ability to expand and penetrate voids, providing tight insulation without any gaps.
4. Light Weight and Ease of Application
It does not add excess weight to structures and surfaces, making it suitable for all types of buildings.
It can be applied quickly using spray tools or insulation panels.
5. Long Lifespan
It is characterized by its durability and ability to withstand long periods without losing its effectiveness.
6. Sound Insulation
It reduces noise transmission between rooms, enhancing comfort inside buildings.
Uses of Foam Insulation
Foam is used in many applications, the most prominent of which are:
source
1. Roof and Wall Insulation
It is used in residential and commercial buildings to prevent heat transfer between the interior and exterior.
It protects walls from moisture absorption and reduces water condensation inside the building.
2. Tank and Pipe Insulation
It prevents water leakage and maintains the water temperature inside the tanks.
It is used in air conditioning and refrigeration systems to maintain pipe efficiency and prevent heat loss.
3. Floor and Foundation Insulation
Reduces heat loss through floors.
Protects foundations from groundwater seepage and moisture.
4. Industrial Facilities and Warehouse Insulation
Maintains the appropriate temperature inside warehouses and industrial buildings.
Reduces operating costs by reducing energy consumption.
How to Apply Foam Insulation
The foam insulation process is carried out in several steps to ensure the highest level of efficiency, including:
1. Surface Preparation
Clean the surface of dust and dirt to ensure proper adhesion of the foam.
Ensure that there are no large cracks that require prior repair.
2. Foam Application
If the foam is in spray form, it is sprayed directly onto the surface using special equipment.
In the case of insulating panels, they are attached using special adhesives or nails.
3. Leveling and Finishing
After applying the foam, it is leveled to ensure even distribution across the surface.
An insulating layer can be added over the foam to increase its durability and resistance to external factors.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Foam Insulation
Foam Type: The appropriate type should be chosen based on the purpose of the insulation (thermal or water).
Thickness and Density: The denser the foam, the greater its insulation efficiency.
Moisture Resistance: It is preferable to choose a foam with high water resistance if the goal is water insulation.
Lifespan: Some types last longer than others, affecting the long-term cost.
Cost and Budget: Foam prices vary based on the type and quality, so the most appropriate solution should be chosen according to the available budget.
Conclusion
Foam insulation is one of the most effective solutions for thermal and water insulation, providing high protection for buildings from environmental factors and reducing energy consumption. Thanks to its variety of types and ease of application, it has become the preferred choice for many construction and industrial projects. However, it is essential to carefully choose the appropriate type and rely on professional technicians to ensure the insulation is applied safely.