Primary Care Physician’s Role in Diabetes Management
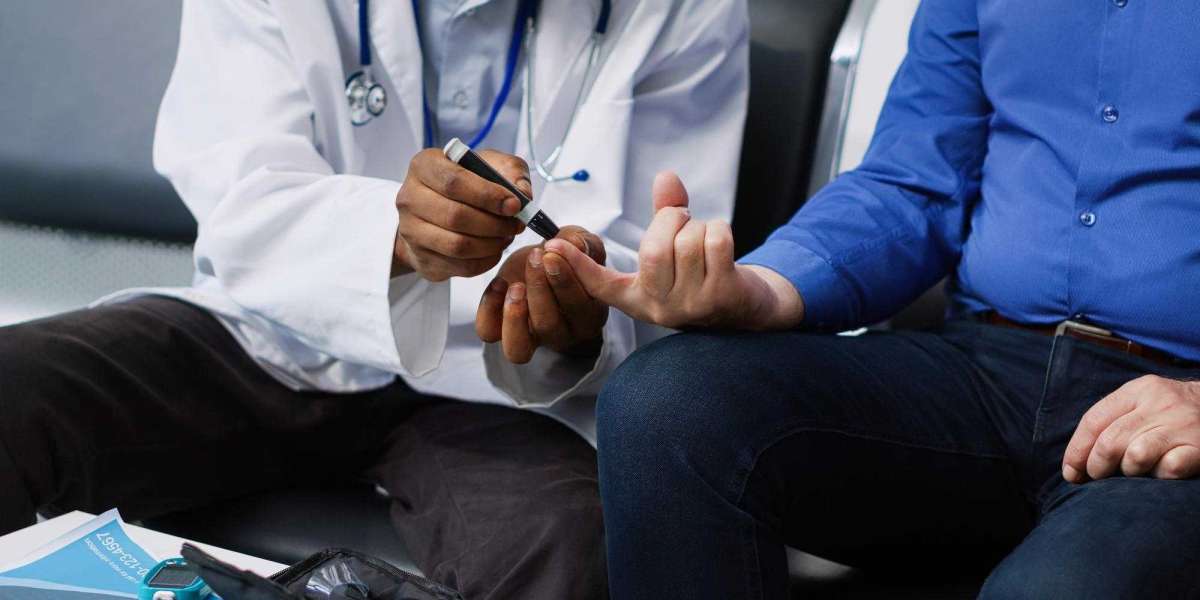
Diabetes, a chronic condition characterized by elevated blood sugar levels, affects millions worldwide. Effective diabetes management requires a multi-faceted approach, and primary care physicians play a crucial role in guiding patients towards optimal health outcomes. This includes not only monitoring blood sugar levels and prescribing medications but also assessing the need for more specialized therapies, such as infusion therapy.
The Importance of Primary Care in Diabetes Management
Primary care physicians serve as the first point of contact for individuals with diabetes. They play a crucial role in:
- Diagnosis and Assessment:
- Conducting thorough medical examinations, including blood tests to assess blood sugar levels, A1c levels, and other relevant markers.
- Identifying potential risk factors and complications associated with diabetes.
- Developing Personalized Treatment Plans:
- Creating individualized treatment plans tailored to each patient’s specific needs, considering factors such as age, lifestyle, and other medical conditions.
- Guiding patients on lifestyle modifications, including dietary changes, exercise regimens, and stress management techniques.
- Medication Management:
- Prescribing and monitoring oral medications, such as metformin, sulfonylureas, and DPP-4 inhibitors.
- Assessing the need for insulin therapy, including injectable insulin and insulin pumps.
- Evaluating the effectiveness of medications and adjusting dosages as needed.
- Monitoring for Complications:
- Regularly monitoring for potential diabetes-related complications, such as heart disease, kidney disease, neuropathy, and eye problems.
- Conducting necessary screenings, such as eye exams, kidney function tests, and nerve conduction studies.
- Providing Education and Support:
- Educating patients about diabetes self-management, including blood sugar monitoring, medication administration, and healthy lifestyle choices.
- Providing emotional and social support to help patients cope with the challenges of living with diabetes.
Tools and Techniques in Diabetes Management
Technology in Diabetes Care
- Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM): Helps track blood sugar levels in real-time.
- Mobile Apps: Assist in medication tracking, meal planning, and logging blood sugar readings.
- Telemedicine: Facilitates remote consultations and follow-ups.
Lifestyle Interventions
PCPs guide patients in making sustainable lifestyle changes, such as adopting healthier eating habits, increasing physical activity, and managing stress.
Preventive Care
Preventing complications is a major focus. PCPs ensure:
- Regular eye exams to detect retinopathy.
- Foot examinations to prevent ulcers and infections.
- Kidney function tests to monitor for nephropathy.
The Future of Diabetes Management in Primary Care
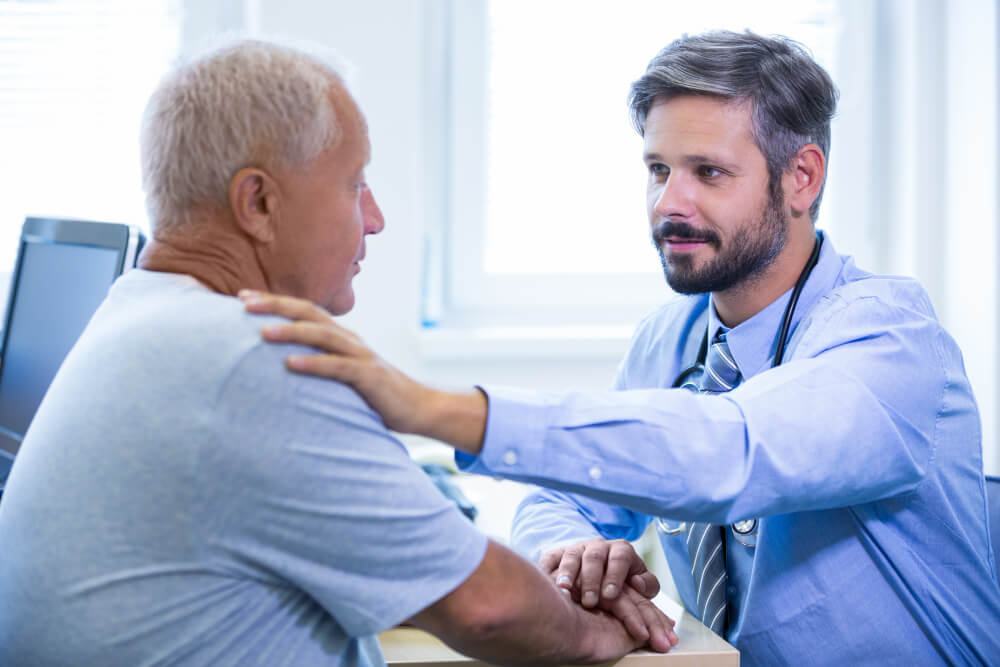

Advances in Treatment
- Innovative Medications: Development of new drugs like GLP-1 receptor agonists and SGLT2 inhibitors.
- Artificial Pancreas Systems: Integrating CGMs with insulin pumps for automated glucose control.
Integrated Care Models
Collaborative care models involving dietitians, diabetes educators, and pharmacists can enhance outcomes.
Focus on Prevention
Primary care is shifting towards prevention, emphasizing early lifestyle interventions and community education programs.
Conclusion
Primary care physicians are indispensable in the fight against diabetes. Through early detection, personalized care, patient education, and coordination with specialists, PCPs ensure comprehensive and effective diabetes management. As the field evolves, embracing new technologies and care models will further empower PCPs to improve patient outcomes and quality of life.
Contact our Primary care physician for diabetes management (972) 937-8900 Or visit us https://sccwaxahachie.com/














