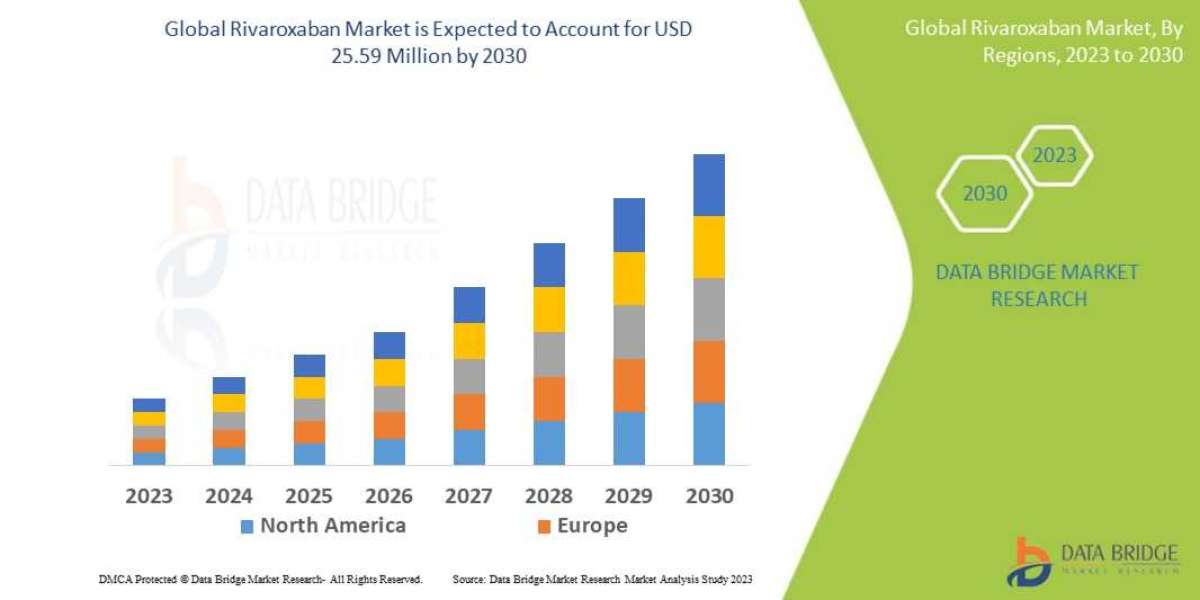
Samsung Electronics, a global technology leader, has firmly established itself as a dominant force in consumer electronics, semiconductors, and telecommunications. Known for its innovation-driven strategy and expansive product portfolio, Samsung continues to shape the global tech landscape. This SWOT analysis delves into the company’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, providing insight into its strategic positioning.
Strengths
1. Diversified Product Portfolio
Samsung's wide-ranging product line spans smartphones, televisions, home appliances, semiconductors, and displays. This diversification reduces dependency on any single product category and enables the company to capture various market segments.
2. Strong Brand Recognition
Ranked among the world’s most valuable brands, Samsung enjoys a solid global reputation for quality, innovation, and design. Its Galaxy smartphone series and QLED TVs are market leaders, reinforcing customer loyalty.
3. Technological Innovation
Samsung consistently invests heavily in RD, leading to breakthroughs in foldable smartphones, 5G technology, and semiconductor manufacturing. The company’s leadership in OLED displays and memory chips underscores its technological edge.
4. Global Manufacturing and Supply Chain Network
Samsung operates an extensive global manufacturing and distribution network. Its vertically integrated supply chain ensures greater control over production costs, quality, and speed to market, enhancing its competitive advantage.
5. Market Leadership in Semiconductors
Samsung SWOT is a dominant player in the memory chip industry (DRAM and NAND flash), supplying critical components for smartphones, data centers, and IoT devices. This segment significantly contributes to the company’s profitability.
Weaknesses
1. Dependence on the Smartphone Market
Despite diversification, Samsung’s heavy reliance on the smartphone segment makes it vulnerable to market saturation, price wars, and shifting consumer preferences, especially in the highly competitive Android market.
2. Legal Disputes and Patent Infringements
Samsung has faced numerous lawsuits related to intellectual property, notably with Apple. These legal challenges result in costly settlements and can tarnish the company’s brand image.
3. Slow Penetration in Software and Services
Samsung’s ecosystem of services and software lags behind competitors like Apple and Google. Its Bixby voice assistant and app ecosystem have struggled to gain significant market traction.
4. Complex Product Ecosystem
The vast product range across various industries can sometimes lead to operational inefficiencies, brand dilution, and inconsistent product quality across regions.
Opportunities
1. Expansion in Emerging Markets
Samsung can capitalize on growing smartphone demand in emerging markets like India, Southeast Asia, and Africa by offering affordable devices tailored to local needs.
2. Growth in 5G and IoT Technologies
As a pioneer in 5G infrastructure and devices, Samsung is well-positioned to lead the adoption of 5G networks globally. Additionally, the expanding IoT market presents opportunities for connected devices and smart home solutions.
3. Semiconductor Demand for AI and Cloud Computing
The rising demand for data centers, AI applications, and electric vehicles is driving growth in semiconductor markets. Samsung can expand its semiconductor business beyond memory to include logic chips and advanced processors.
4. Sustainability and Green Technologies
Growing environmental concerns offer Samsung the opportunity to invest in eco-friendly products and sustainable manufacturing. The company can enhance its reputation by adopting green technologies and reducing its carbon footprint.
5. Strategic Partnerships and Acquisitions
Samsung can strengthen its market position by forming strategic alliances and acquiring innovative startups in artificial intelligence, health tech, and autonomous vehicles. These investments can diversify revenue streams.
Threats
1. Intense Market Competition
Samsung faces fierce competition from global and regional brands across all segments. In smartphones, Apple, Huawei, Xiaomi, and Oppo challenge its market share. In semiconductors, it competes with Intel, TSMC, and Micron.
2. Geopolitical and Trade Tensions
Trade disputes between major economies, such as the U.S. and China, can disrupt Samsung's global supply chain. Tariffs and export restrictions on semiconductor components pose significant operational risks.
3. Rapid Technological Changes
The fast-paced technology industry demands constant innovation. Failure to anticipate or adapt to emerging technologies like foldable devices, augmented reality, or blockchain could weaken Samsung’s market leadership.
4. Currency Fluctuations
As a multinational corporation, Samsung’s profitability is sensitive to currency exchange rate volatility, particularly between the Korean won and major global currencies.
5. Supply Chain Disruptions
Global crises, such as the COVID-19 pandemic, have exposed vulnerabilities in supply chains. Component shortages, especially in semiconductors, could delay product launches and impact revenue.
Conclusion
Samsung Electronics' impressive strengths in innovation, brand equity, and global operations position it as a leader in the technology industry. By leveraging opportunities in 5G, semiconductors, and emerging markets, Samsung can sustain long-term growth. However, it must navigate challenges from intense competition, legal issues, and geopolitical risks. Strategic investments in software ecosystems, sustainability, and advanced technologies will be crucial for maintaining its competitive edge and securing future success.