Introduction
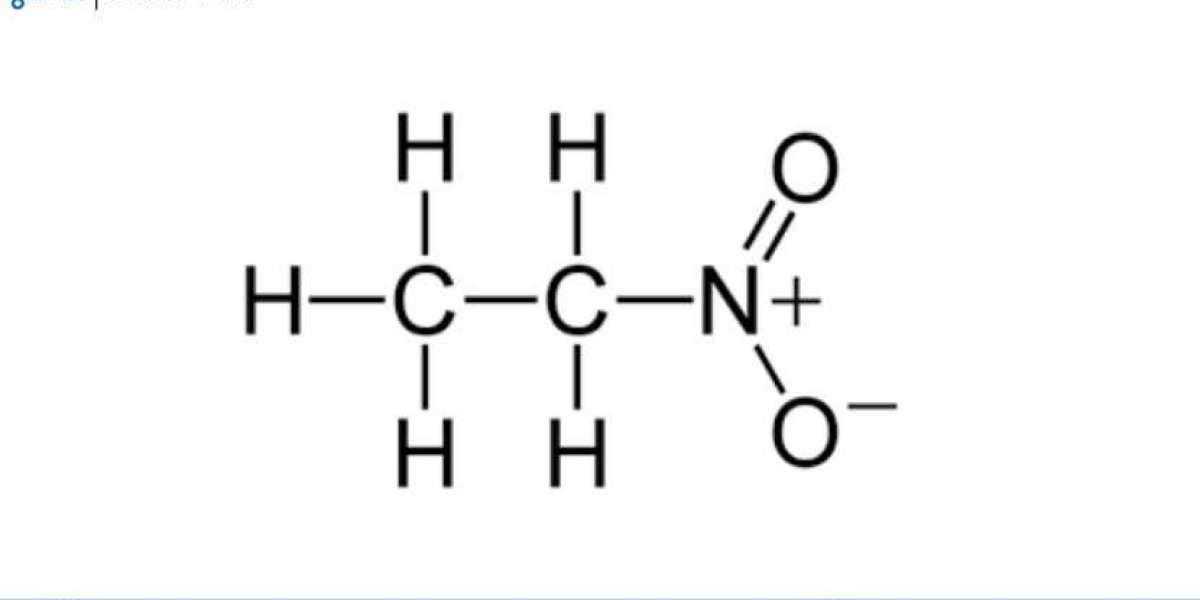
Nitroethane is an organic compound with the chemical formula C2H5NO2, typically used as a solvent, in the manufacture of high-performance fuels, as a chemical intermediate, and in the production of various chemicals such as plastics, coatings, and adhesives. Nitroethane is a versatile compound used in a variety of industries due to its high stability and reactivity. The Nitroethane Manufacturing Plant Project Report provides an in-depth look into setting up a production facility for nitroethane, detailing the raw materials required, the manufacturing process, machinery, market potential, financial projections, and regulatory considerations.
This report is essential for entrepreneurs and investors interested in entering the nitroethane production sector, offering guidance on establishing a plant that meets the growing demand for this chemical.
Market Overview
The global nitroethane market has witnessed consistent growth due to its wide range of applications across various industries. It is used extensively in the chemical, automotive, and pharmaceutical industries, as well as in the production of specialty fuels for racing and aviation. Nitroethane’s use as a solvent and an intermediate compound for the synthesis of other chemicals further supports the demand.
Key Drivers of Market Growth:
- Chemical Manufacturing: Nitroethane serves as a crucial building block in the production of numerous chemicals, including explosives, agrochemicals, and specialty polymers. The growing chemical manufacturing sector is driving demand for this compound.
- Automotive Industry: Nitroethane is utilized in the automotive industry, particularly in high-performance fuels, such as those used in racing and aviation, contributing to market growth.
- Pharmaceutical Industry: Nitroethane is also used as a solvent and intermediate in the pharmaceutical industry, where it is part of the production of various drugs.
- Increasing Demand for Specialty Chemicals: Nitroethane is essential in many specialized chemical processes, such as the production of coatings, adhesives, and plasticizers, further boosting its demand.
As global industrialization continues, particularly in emerging economies, the demand for nitroethane in chemical processes and as a solvent is expected to grow, providing a profitable opportunity for businesses in this field.
Get a Free Sample Report with Table of Contents@
Raw Materials
The primary raw materials for producing nitroethane are ethanol and nitric acid, both of which are readily available in the global market. Below are the key materials used in the manufacturing process:
1. Ethanol (C2H5OH)
Ethanol, a simple alcohol, is the key starting material for the production of nitroethane. It is used because of its readily available hydrocarbon structure that can easily undergo nitration. Ethanol is derived from a variety of sources, including natural gas, petroleum, and biomass.
2. Nitric Acid (HNO3)
Nitric acid is used to nitrate ethanol, producing nitroethane. It serves as the nitrating agent in the process. High-purity nitric acid is typically used to ensure the production of high-quality nitroethane.
3. Catalysts
A variety of catalysts may be used to enhance the reaction between ethanol and nitric acid, improving yields and the efficiency of the production process. These catalysts help in controlling reaction conditions, such as temperature and pressure.
4. Solvents
Solvents may be used to assist in the mixing of ethanol and nitric acid, ensuring proper interaction between the chemicals and facilitating the nitration process.
Production Process
The production of nitroethane primarily involves a nitration process, where ethanol is reacted with nitric acid. Below is a step-by-step overview of the manufacturing process:
1. Nitration Reaction
The first and primary step in nitroethane production is the nitration of ethanol. This involves the addition of ethanol to a nitrating mixture, usually nitric acid and sulfuric acid. The nitrating mixture generates the nitronium ion (NO2+), which is responsible for reacting with ethanol. The reaction results in the formation of nitroethane and water.
2. Separation and Purification
After the nitration reaction is complete, the reaction mixture contains a mixture of nitroethane, unreacted ethanol, nitric acid, and by-products. Separation and purification processes are required to isolate and purify the nitroethane. This may involve distillation, where the components are separated based on differences in boiling points, followed by additional purification steps such as washing with water and neutralization.
3. Neutralization and Filtration
After separating the crude nitroethane, any residual acidic or basic impurities must be neutralized. Typically, water or dilute sodium bicarbonate solutions are used to neutralize remaining acids. The solution is then filtered to remove any solid contaminants.
4. Drying and Packaging
Once the nitroethane has been purified, it is typically dried to remove any remaining moisture before being packaged for storage or shipment. Drying is an essential step to ensure the chemical’s stability and quality. Nitroethane is usually stored in sealed containers to prevent contamination and maintain its quality.
Machinery and Equipment
To set up a manufacturing plant for nitroethane, the following key equipment is required to handle the raw materials, ensure safety, and produce high-quality nitroethane efficiently:
1. Reactor Vessel
The nitration process takes place in a reactor vessel, where ethanol reacts with nitric acid under controlled conditions. The reactor must be designed to withstand high temperatures and pressures and be constructed from materials that are resistant to corrosion from nitric acid.
2. Distillation Column
A distillation column is used to separate the nitroethane from other components in the reaction mixture based on differences in boiling points. This is one of the most crucial pieces of equipment in ensuring the purity of the final product.
3. Cooling System
The nitration reaction is exothermic, meaning it releases heat. A cooling system is necessary to control the temperature inside the reactor vessel and prevent runaway reactions or overheating.
4. Filtration Units
Filtration units are used to remove solid by-products and impurities from the reaction mixture after the nitration process. These may include vacuum filtration systems or centrifuges, depending on the nature of the materials being filtered.
5. Drying Equipment
After purification, drying equipment such as rotary dryers or vacuum ovens is used to remove any excess moisture from the nitroethane.
6. Storage Tanks
Specialized storage tanks are required to store the finished nitroethane. These tanks must be made from materials that are compatible with the chemical properties of nitroethane to avoid corrosion or degradation.
7. Safety Equipment
Given the highly reactive and hazardous nature of the materials involved in nitroethane production, safety equipment such as explosion-proof systems, gas detectors, and emergency response equipment must be installed throughout the plant.
Financial Projections and Cost Estimation
Establishing a nitroethane manufacturing plant requires careful financial planning. Key cost components include:
1. Capital Expenditure (CAPEX)
- Facility Setup: Costs for acquiring land, constructing the plant, and installing infrastructure, including utilities and waste management systems.
- Machinery and Equipment: Investment in reactor vessels, distillation columns, filtration units, and drying equipment.
- Raw Materials: Initial procurement of ethanol, nitric acid, and catalysts.
2. Operating Expenditure (OPEX)
- Raw Materials: Ongoing costs for purchasing ethanol and nitric acid to ensure continuous production.
- Labor Costs: Wages for workers, including operators, technicians, and administrative staff.
- Energy and Utilities: Costs associated with electricity, water, and heating required for the production process.
- Maintenance: Regular maintenance of equipment and machinery to prevent downtime and ensure smooth operation.
3. Revenue Generation
Revenue will primarily come from the sale of nitroethane to industries such as chemicals, pharmaceuticals, automotive, and specialty chemical production. The pricing will depend on market conditions, the quality of the nitroethane produced, and the scale of production.
4. Return on Investment (ROI)
A comprehensive financial plan should include projected sales volumes, profit margins, and break-even analysis. The time frame for recouping the initial investment and achieving profitability will depend on factors such as production capacity, operating efficiency, and market demand.
Regulatory and Legal Considerations
The production of nitroethane is subject to strict environmental, health, and safety regulations. Compliance with these regulations is crucial to the successful operation of a manufacturing plant.
1. Environmental Regulations
Manufacturers must comply with local environmental laws regarding emissions, waste disposal, and chemical handling. Proper waste management systems must be in place to handle by-products and any hazardous materials involved in the production process.
2. Health and Safety Standards
The chemicals involved in the production of nitroethane, such as nitric acid, are highly hazardous. Therefore, safety measures such as proper ventilation, protective equipment, and training programs for workers are essential. Compliance with OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) standards is mandatory.
3. Quality Control
Nitroethane must meet various quality standards, particularly if it is being used in sensitive applications such as pharmaceuticals or automotive fuels. Manufacturers must implement stringent quality control procedures to ensure consistency and purity.
Media Contact
Company Name: Claight Corporation
Contact Person: Lewis Fernandas, Corporate Sales Specialist — U.S.A.
Email: sales@expertmarketresearch.com
Toll Free Number: +1–415–325–5166 | +44–702–402–5790
Address: 30 North Gould Street, Sheridan, WY 82801, USA
Website: www.expertmarketresearch.com
Aus Site: https://www.expertmarketresearch.com.au