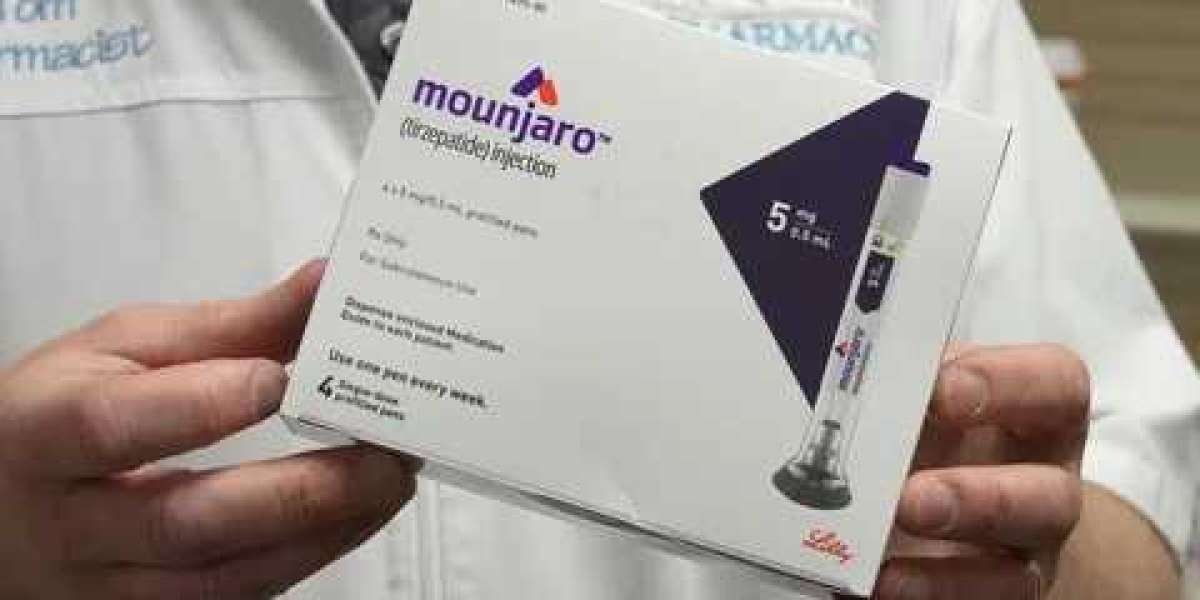
Managing glucose levels effectively is essential for individuals living with Type 2 diabetes, a condition that can lead to serious complications if left unchecked. The Monjaro injection is an exciting new treatment option that is revolutionizing the way we approach blood sugar control and metabolic health. By targeting the underlying processes that regulate glucose metabolism, Monjaro is showing great promise in helping patients manage their condition more effectively.
In this blog, we’ll dive into the science behind Monjaro injections حقن مونجارو , exploring how they work on a molecular level to improve glucose metabolism and help individuals achieve better control over their blood sugar levels.
What is Monjaro Injection?
Monjaro (tirzepatide) is an injectable medication that has recently received attention for its innovative approach to treating Type 2 diabetes. Unlike traditional diabetes treatments, Monjaro is a dual-action medication that mimics the function of two key hormones involved in glucose regulation: GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide-1) and GIP (glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide). These hormones play a critical role in regulating blood sugar levels, and by targeting both of them, Monjaro can offer more comprehensive blood sugar control than single-hormone treatments.
How Does Monjaro Injection Influence Glucose Metabolism?
The body’s ability to regulate glucose is complex, involving several hormones that interact with various organs, including the pancreas, liver, and intestines. Let’s break down how Monjaro affects glucose metabolism and why this dual-action approach is so powerful.
1. GLP-1: Enhancing Insulin Secretion and Reducing Glucagon
GLP-1 is a hormone produced in the intestines in response to food intake. It stimulates the pancreas to release insulin when blood sugar levels are high, helping cells absorb glucose and lower blood sugar. At the same time, GLP-1 suppresses the release of glucagon, a hormone that typically signals the liver to release stored glucose into the bloodstream, raising blood sugar levels.
By activating the GLP-1 receptor, Monjaro increases insulin secretion and decreases glucagon release, helping regulate blood glucose more effectively. This action helps maintain stable blood sugar levels and prevents hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) after meals.
2. GIP: Enhancing Insulin Secretion and Regulating Fat Metabolism
GIP is another hormone that plays a role in glucose metabolism. Like GLP-1, GIP stimulates insulin secretion when blood glucose levels rise. However, GIP also helps regulate fat metabolism, influencing how the body stores and uses fat. GIP’s impact on fat cells has the potential to aid in weight loss, which is crucial for managing Type 2 diabetes, as excess body weight can impair insulin sensitivity.
The dual activation of both GLP-1 and GIP receptors by Monjaro means that the medication not only enhances insulin secretion but also helps improve fat metabolism, contributing to weight loss and better glucose control.
The Effects of Monjaro on Glucose Control
1. Improved Blood Sugar Regulation
By targeting both GLP-1 and GIP receptors, Monjaro offers a more efficient way to regulate blood sugar compared to traditional diabetes treatments. Clinical studies have shown that Monjaro significantly reduces HbA1c levels (a long-term marker of blood sugar control), often by more than 2%. This is a substantial improvement for many people with Type 2 diabetes who may struggle to achieve good blood sugar control with other medications.
Moreover, Monjaro works across the entire day, not just after meals, ensuring stable blood glucose levels and minimizing the risk of blood sugar fluctuations that can lead to complications.
2. Reduced Appetite and Weight Loss
One of the secondary benefits of Monjaro’s action on GLP-1 is appetite suppression. GLP-1 helps slow gastric emptying, which can make patients feel fuller for longer and reduce hunger cravings. As a result, many individuals experience weight loss when using Monjaro in combination with other lifestyle changes such as diet and exercise.
For people with Type 2 diabetes, losing weight is especially beneficial because it can improve insulin sensitivity and further help regulate blood sugar levels. In fact, many individuals using Monjaro report weight loss as a positive side effect, which contributes to overall metabolic health.
3. Lower Risk of Hypoglycemia
Another key advantage of Monjaro over some other diabetes medications is its low risk of causing hypoglycemia (dangerously low blood sugar levels). Since Monjaro works by stimulating insulin secretion only when blood glucose levels are high, it helps to prevent the excessive insulin release that can lead to hypoglycemia. This makes Monjaro a safer option for many patients, especially those who are concerned about the risks of low blood sugar.
Clinical Studies and Real-World Impact
The benefits of Monjaro injections are not just theoretical; they have been supported by clinical research. In large-scale clinical trials, Monjaro has demonstrated its ability to significantly improve glycemic control, with many patients experiencing a reduction in HbA1c levels, weight loss, and better overall metabolic health.
In addition to clinical trials, real-world experiences from patients using Monjaro have been overwhelmingly positive. Many individuals report feeling more energetic, experiencing fewer blood sugar spikes, and noticing improvements in their overall health as they manage their diabetes with Monjaro.
How to Use Monjaro Injection
Monjaro injection is administered subcutaneously (under the skin) once a week. It is available as a pre-filled pen, making it easy for patients to administer the injection themselves at home after proper training from a healthcare professional. The convenience of a once-weekly injection is one of the reasons why Monjaro has become so popular among patients.
Before starting Monjaro, patients should consult their healthcare provider to ensure that the medication is appropriate for their specific condition. Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels, weight, and overall health will help ensure the treatment is working effectively.
Side Effects and Considerations
Like any medication, Monjaro can cause side effects, although they are generally mild and transient. The most common side effects are gastrointestinal, such as nausea, diarrhea, and constipation, especially when starting the medication. These side effects typically improve over time as the body adjusts to the medication.
As with any diabetes treatment, it’s important to follow your healthcare provider’s guidance and report any unusual or severe side effects. Your doctor will monitor your progress and may adjust your dosage if necessary to ensure the best outcomes.
Conclusion
Monjaro injection represents a major advancement in diabetes treatment, providing a dual-action approach to glucose regulation that is more effective than many traditional therapies. By targeting both GLP-1 and GIP receptors, Monjaro helps improve blood sugar control, reduces appetite, promotes weight loss, and offers a safer treatment option with a low risk of hypoglycemia.