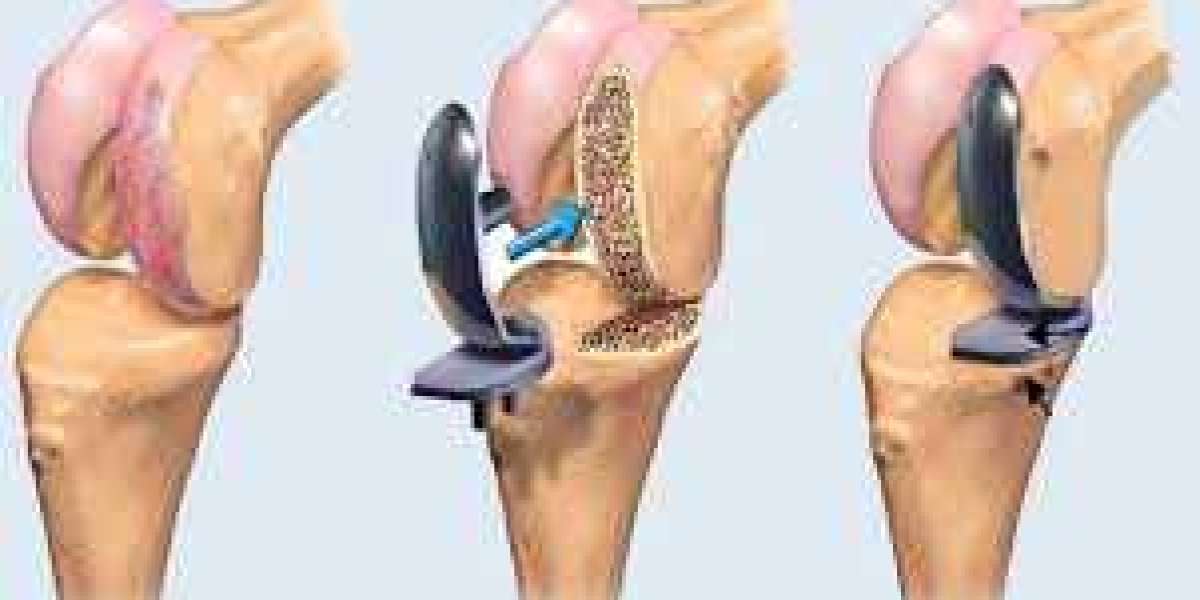
Knee replacement surgery is a common and effective procedure for individuals suffering from chronic knee pain or arthritis. It can significantly improve quality of life, offering pain relief and enhanced mobility. However, if you are pregnant or planning to become pregnant, you might be wondering whether undergoing knee replacement surgery during pregnancy is a safe option. In this post, we will explore why knee replacement surgery is generally not recommended during pregnancy and discuss the associated risks and considerations.
Why Knee Replacement Surgery Is Not Recommended During Pregnancy
While knee replacement surgery is highly effective for those with debilitating knee conditions, it’s typically postponed until after pregnancy. The main reasons for this are the potential risks to both the mother and the developing fetus. Let’s look at these risks more closely.
1. Anesthesia Risks
Anesthesia is a crucial part of knee replacement surgery, as it ensures the patient remains comfortable and pain-free during the procedure. However, the types of anesthesia used for surgery may pose risks to a developing fetus, especially during the early stages of pregnancy. General anesthesia, which is often used for knee replacements, can potentially interfere with fetal development. In particular, there are concerns about the effects of certain medications on the baby’s organ development, especially during the first trimester when organs are still forming.
For these reasons, many doctors are cautious about performing surgeries requiring anesthesia on pregnant women. While regional anesthesia, such as spinal blocks, can sometimes be used for joint surgeries, it’s not always ideal for knee replacements and comes with its own set of risks.
2. Infection Risks
All surgeries carry the risk of infection, but this concern is particularly important during pregnancy. Infections can complicate both the health of the mother and the developing baby. In addition to the possibility of a wound infection at the surgical site, deep infections in the joint could require further interventions, including prolonged courses of antibiotics or additional surgeries.
Pregnant women may be more susceptible to certain infections, and treatment options may be limited depending on the stage of pregnancy. The need for more invasive procedures or medication could present complications for the pregnancy and the baby, making it essential to carefully consider the timing of knee replacement surgery.
3. Blood Clot Risks
Blood clots are a serious risk after knee replacement surgery, and pregnancy itself increases the risk of clot formation. Deep vein thrombosis (DVT), which involves blood clots forming in the deep veins of the legs, is a known risk after joint replacement surgery. If a clot travels to the lungs, it can cause a pulmonary embolism, which is life-threatening. Pregnancy increases the likelihood of developing DVT, and undergoing knee replacement surgery while pregnant further heightens the risk.
While blood clot prevention measures are typically taken after surgery, such as blood-thinning medications or physical therapy, managing these risks during pregnancy can be more complicated. Doctors must consider how to balance clot prevention with the potential effects on the pregnancy and the health of the mother.
4. Recovery Challenges During Pregnancy
Recovery from knee replacement surgery is a significant process that requires time, physical therapy, and mobility. After the procedure, patients must engage in physical therapy to regain strength, flexibility, and joint movement. For someone who is pregnant, this recovery process can be more challenging.
Pregnancy can place additional strain on the body, and healing from knee replacement surgery requires energy and mobility, which may be difficult when managing the physical demands of pregnancy. The need to walk, rest, and participate in therapy can make it harder to recover fully and comfortably. Furthermore, managing the additional physical discomforts of pregnancy, such as fatigue, swelling, or back pain, can interfere with the healing process.
Additionally, certain physical therapy exercises may need to be modified to accommodate pregnancy, making it harder to reach full recovery. In some cases, the need for mobility aids or support during pregnancy could complicate the recovery process even further.
When Can Knee Replacement Surgery Be Considered During Pregnancy?
While it’s generally advised to wait until after pregnancy to undergo knee replacement surgery, there are certain situations where surgery might be necessary or considered. In cases where a woman’s knee condition is causing extreme pain or disability, and non-surgical treatments like medication or physical therapy haven’t been effective, a doctor may need to evaluate whether knee replacement is urgent.
For example, if a pregnant woman is suffering from significant joint deformity or pain that prevents her from performing daily activities, the decision to proceed with surgery could be considered. In these cases, the timing of the surgery would be carefully evaluated based on the stage of pregnancy, the severity of the knee condition, and the potential risks to both the mother and baby.
In such rare cases, the orthopedic surgeon would collaborate closely with an obstetrician to ensure that the pregnancy is carefully monitored and that the surgery is done with the least risk to the mother and fetus. The surgery might also be delayed until the second trimester, when the risk of complications from anesthesia and other factors is lower. However, in most cases, the decision would be to wait until after childbirth.
The Importance of Consulting Both Specialists
If you are pregnant or planning to become pregnant and are considering knee replacement surgery, it’s crucial to consult both your orthopedic surgeon and obstetrician. Each specialist will have a unique perspective on the potential risks and benefits and can provide guidance on the best course of action for your health.
Your orthopedic surgeon will assess the severity of your knee condition and whether surgery is necessary, while your obstetrician will evaluate your pregnancy to ensure that any decision regarding surgery prioritizes both your health and the well-being of your baby. Together, they will create a plan that minimizes risks and optimizes recovery.
Conclusion
In most cases, knee replacement surgery during pregnancy is not recommended due to the potential risks associated with anesthesia, infections, blood clots, and recovery complications. However, in certain cases where the knee condition is severely impairing daily life, the procedure might be considered with careful monitoring. Always consult your healthcare team to ensure the best decision is made for your health and your pregnancy. If knee replacement is necessary, waiting until after childbirth is typically the safest approach.
Follow the links for more other treatment information :-
https://www.edhacare.com/treatments/orthopedic/knee-replacement
https://www.edhacare.com/sw/blogs/intestine-swelling-symptoms/
https://www.edhacare.com/treatments/gynecology/cardiotocography-ctg
https://www.edhacare.com/sw/blogs/common-seizure-symptoms-and-their-causes/
https://www.edhacare.com/blogs/early-stages-of-stomach-cancer/
https://www.edhacare.com/treatments/nephrology/hydronephrosis
https://www.edhacare.com/doctors
https://www.edhacare.com/sw/blogs/early-stages-of-stomach-cancer/
https://www.edhacare.com/sw/treatments/cancer/anal-cancer
https://www.edhacare.com/sw/blogs/how-to-cure-tonsils-permanently/
https://www.edhacare.com/blogs/uncovering-the-early-stage-ascites-symptoms/
https://www.edhacare.com/ar/treatments/gynecology/bartholins-cyst-treatment
https://www.edhacare.com/treatments/gynecology/cardiotocography-ctg
https://www.edhacare.com/ar/treatments/gynecology/ovarian-cyst-removal
https://www.edhacare.com/ar/blogs/advancements-in-pulmonary-fibrosis-treatment/
https://www.edhacare.com/ar/treatments/gynecology/hymenotomy
https://www.edhacare.com/ar/blogs/hymenoplasty-treatment-cost-in-turkey/
https://www.edhacare.com/ar/blogs/early-signs-of-leukemia-in-adults/
https://www.edhacare.com/ar/treatments/urology/nephrectomy-surgery
https://www.edhacare.com/ar/blogs/what-is-psoriasis-autoimmune-disease/
https://www.edhacare.com/ar/treatments/gynecology/intrauterine-device-placement